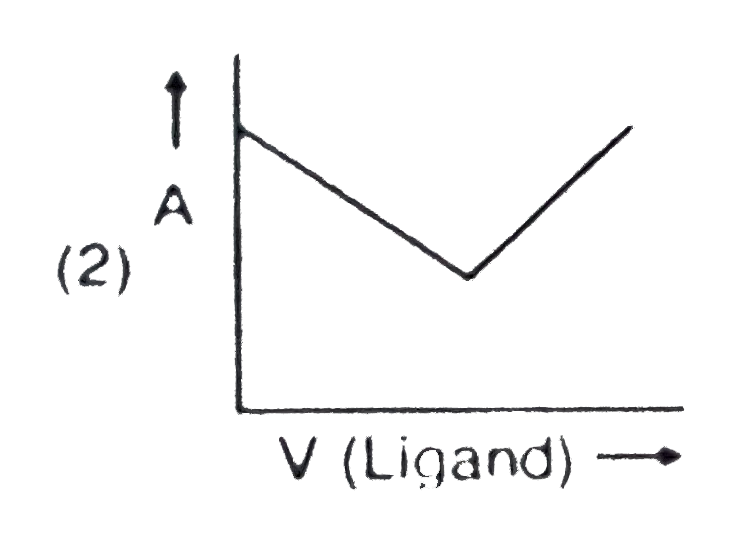A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
COORDINATION COMPOUNDS
RESONANCE|Exercise Additional Problem for Self Practice (APSP) Part-I|30 VideosCOORDINATION COMPOUNDS
RESONANCE|Exercise Additional Problem for Self Practice (APSP) Part-II|68 VideosCOORDINATION COMPOUNDS
RESONANCE|Exercise Exercise-3 Part-II: JEE(Main ) /AIEEE Problem|36 VideosCHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFE
RESONANCE|Exercise ORGANIC CHEMISTRY(Chemistry in every day life)|31 VideosD & F BLOCK ELEMENTS
RESONANCE|Exercise INORGANIC CHEMISTRY(d & f- Block Elments)|40 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-COORDINATION COMPOUNDS-Exercise-3 Online Exam
- Which of the following name formula combinations is not correct ?
Text Solution
|
- Consider the coordination compound , [Co(NH(3))(6)]Cl(3). In the forma...
Text Solution
|
- Among the following species the one which causes the highest CFSE, De...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following complexes will mostly likely abosorb visible li...
Text Solution
|
- An octahedral complex with molecular composition M.5NH(3).Cl.SO(4) has...
Text Solution
|
- Nickel (Z=28) combines with a uninegative monodenatate ligands to for...
Text Solution
|
- The correct statement on the isomerism associated with the following c...
Text Solution
|
- Which molecule/ion among the following cannot act as a ligand in compl...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following complex ions has electrons that are symmetrical...
Text Solution
|
- Identify the correct trend given below : ( Atomic no : Ti=22, Cr=24 an...
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following complexes will consume more equivalent of a...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following is an example of homoleptic complex ?
Text Solution
|
- sp^(3)d^(2) hybridization is not displayed by :
Text Solution
|
- [Co(2)(CO)(8)] displays :
Text Solution
|
- The correct combination is :
Text Solution
|
- The correct order of spin-only magnetic moments among the following is...
Text Solution
|
- The total number of possible isomers of sqaure-planar [Pt(Cl)(NO(2))(N...
Text Solution
|
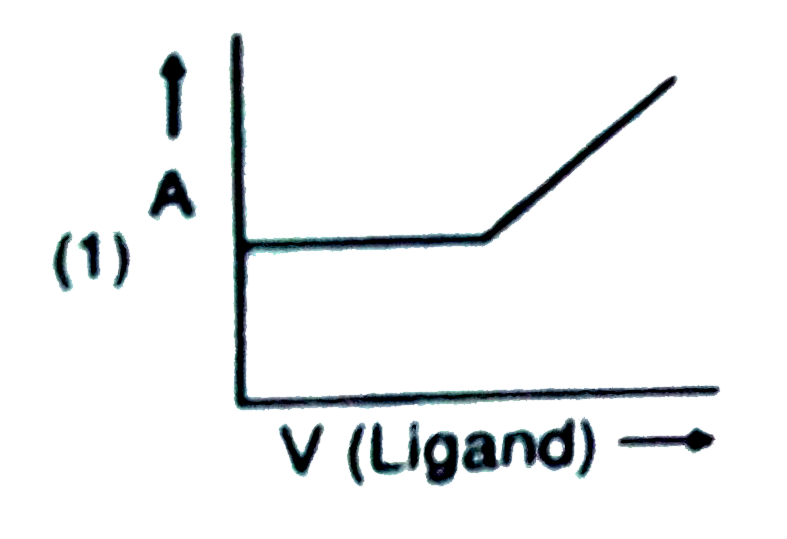
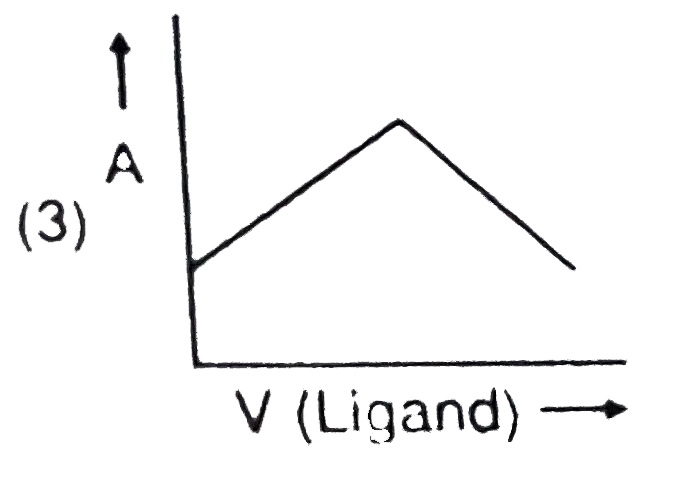
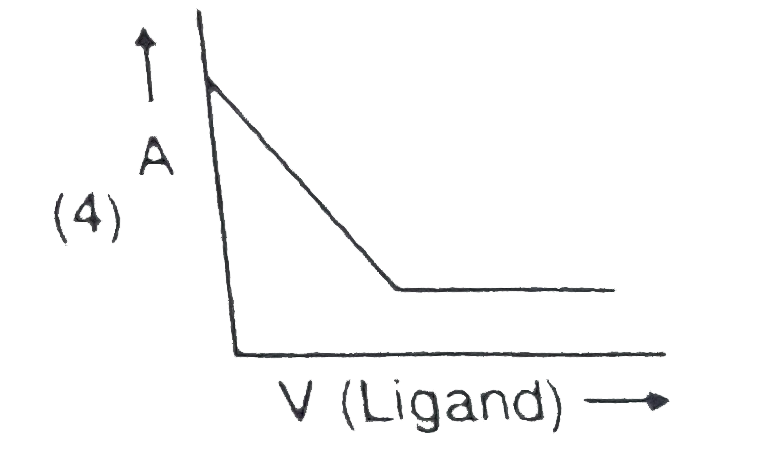
- In a complexometric titration of metal ion with ligand M("Metal ion"...
Text Solution
|
- In Wilkinson's catalyst, the hybridization of central metal ion and it...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following complexes will show geometrical isomerism ?
Text Solution
|