Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
STEREOISOMERISM
RESONANCE|Exercise EXERCISE (PART III : ONE OR MORE THAN ONE OPTIONS CORRECT TYPE)|14 VideosSTEREOISOMERISM
RESONANCE|Exercise EXERCISE (PART IV : COMPREHENSION)|5 VideosSTEREOISOMERISM
RESONANCE|Exercise EXERCISE (PART I ONLY ONE OPTION CORRECT TYPE)|10 VideosSOLUTIONS
RESONANCE|Exercise Advabced Level Problems (PART-2)|35 VideosSTRUCTURAL IDENTIFICATION
RESONANCE|Exercise Advanced level Problems (Part-III)|12 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESONANCE-STEREOISOMERISM-EXERCISE (PART II : SINGLE AND DOUBLE VALUE INTEGER TYPE)
- How many cyclic isomers isomers (structrural and geometrical only) exi...
Text Solution
|
- In given compounds how many can show geometrical isomerism : ,
Text Solution
|
- In given compounds how many have Z configuration along double bond ?
Text Solution
|
- Sum of C(2) & C(3) axis of symmetry is
Text Solution
|
- Pure cholesterol has a specific rotation of -32. A sample of choleste...
Text Solution
|
- Pure (R) Mandelic acid has specific rotation of 150. If a sample con...
Text Solution
|
- Total number of geometrical isomers in the given compound are
Text Solution
|
- Total number of geometrical isomers in the given compound are :
Text Solution
|
- Total number of stereoisomers of compound CH(3)-CH=CH-underset(overset...
Text Solution
|
- Total number of optically active stereoisomers of CH(3)-underset(overs...
Text Solution
|
- For the compound A-CH(2)-CH(27)-A draw the newman projection formula o...
Text Solution
|
- Total number of stereoisomers possible for the given structure excludi...
Text Solution
|
- Observe the compound 'M' If in this compound X=Total number of ...
Text Solution
|
- How many of the following are cis dichlorocyclohexane.
Text Solution
|
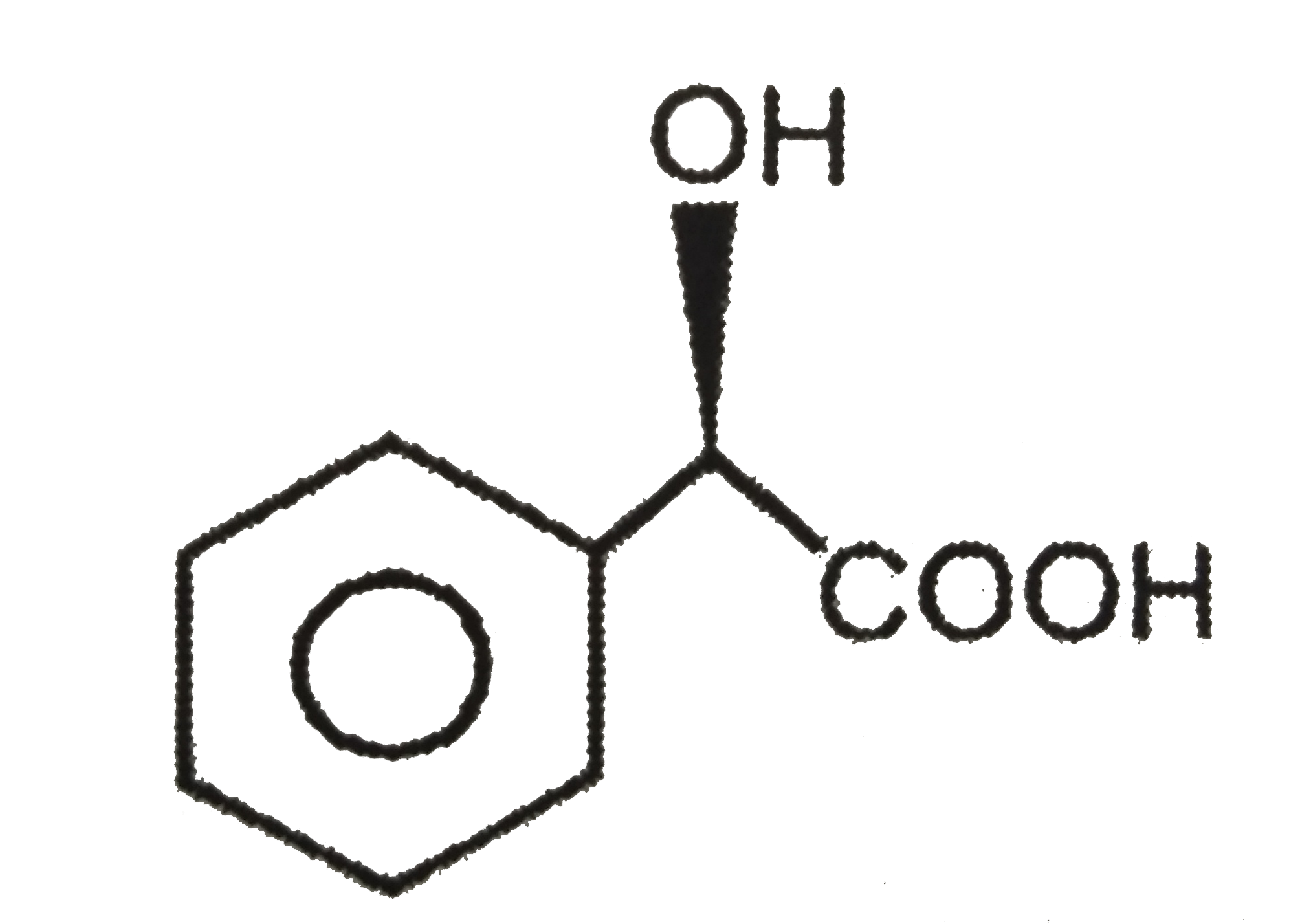 has specific rotation of 150. If a sample contains 60% of the R and 40% of its enantiomer, the `[alpha]` of his solution is.
has specific rotation of 150. If a sample contains 60% of the R and 40% of its enantiomer, the `[alpha]` of his solution is.