Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise REVISION EXERCISES (Very Short Answer Questions Carrying 1 mark)|29 VideosSYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise REVISION EXERCISES (Additional Questions Carrying 1 mark )|4 VideosSYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise NCERT FILE (NCERT EXEMPLAR PROBLEMS (SUBJECTIVES QUESTIONS) (Very Short Answer Type Questions))|9 VideosPHYSICAL WORLD
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise Revision exercises (Long answer questions)|6 VideosTHERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER PRACTICE TEST|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MODERN PUBLICATION-SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION-HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS & ADVANCED LEVEL QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS
- Two charged particles of masses m and 2m are placed distane d apart o...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a gravity free hall in which a tray of mas M, carrying a cubi...
Text Solution
|
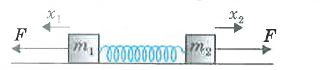
- Two blocks m(1) and m(2) are connected by a spring of force constant ...
Text Solution
|
- The system described in previous question is kept on a frictionless ho...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m is placed at rest on the top of a smooth wedge of...
Text Solution
|
- Monkey of mass m is holding the end of string connected to a balloon o...
Text Solution
|
- String going over a pulley connects two blocks of masses m, and my. St...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of radis R is cut out from a larger disc of radius 2R in such a...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses m, and m, are connected to the ends of a spring o...
Text Solution
|
- A ladder of mass 20 kg is resting against a vertical smooth wall. Ladd...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of mass m and length l is at rest on smooth horizontal s...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere of mass m and radius R is kept on a rough horizontal floor. C...
Text Solution
|
- String is wrapped over a pulley and free end is fixed to the ceiling a...
Text Solution
|