Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise PRACTICE PROBLEM|28 VideosTHERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise CONCEPTUAL QUESTIONS|16 VideosSYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise Chapter Practice Test (for Board Examination)|16 VideosUNITS AND MEASUREMENT
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER PRACTICE TEST|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MODERN PUBLICATION-THERMAL PROPERTIES OF MATTER-CHAPTER PRACTICE TEST
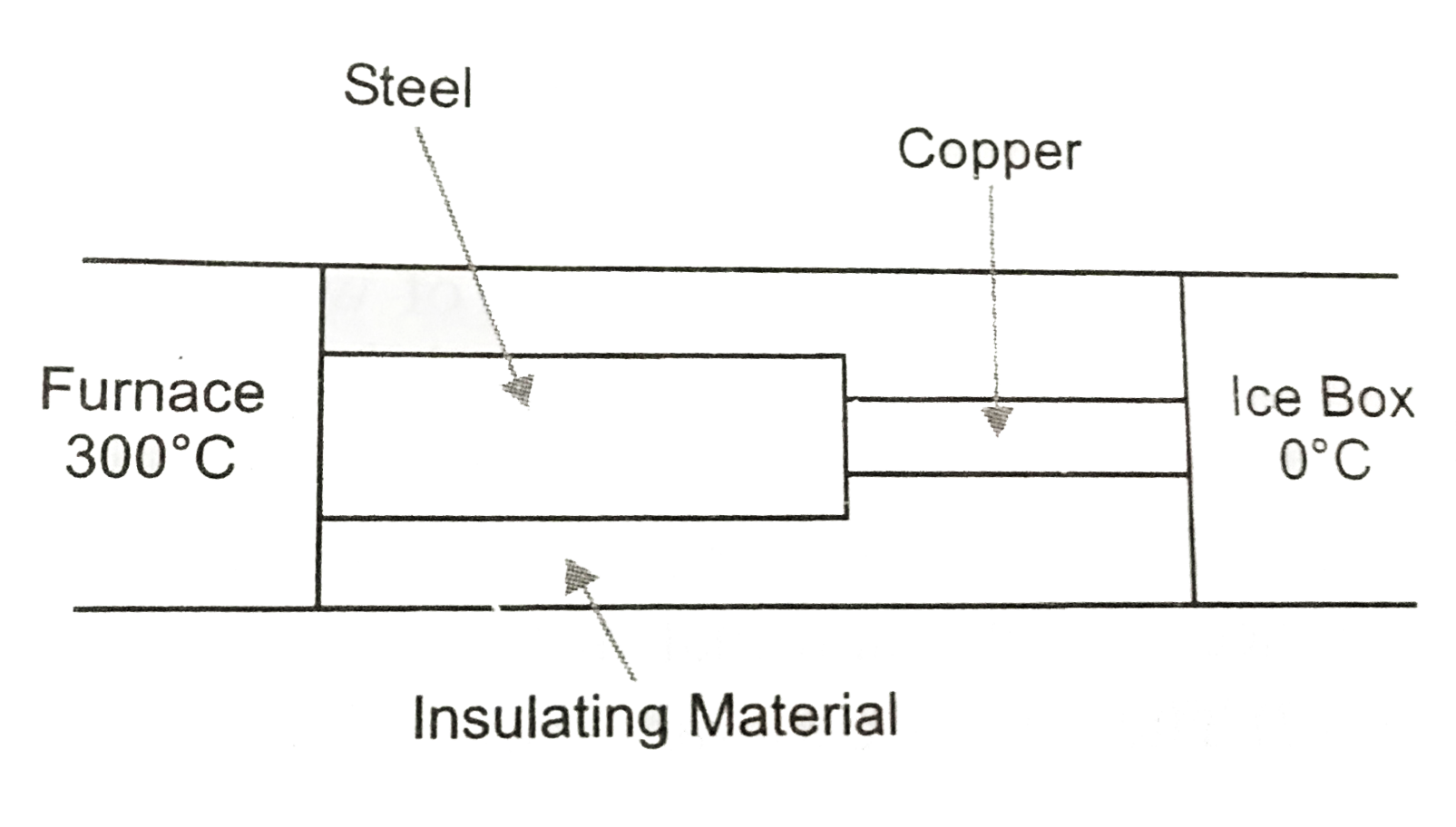
- What is the temperature of steel-copper junction in the steady state o...
Text Solution
|
- Why burns from steam are more serious than those from boling water?
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds can be used as antifreeze in automobi...
Text Solution
|
- What is specific heat of a gas is an isothermal process?
Text Solution
|
- What is the principle of calorimetry.
Text Solution
|
- Is J a physical constant or a conversion factor?
Text Solution
|
- Animals curl into a ball, when they feel very cold.
Text Solution
|
- Water is heated from below but not from top. Why?
Text Solution
|
- Is the rate of cooling the same thing as the rate of loss of heat? Exp...
Text Solution
|
- State Stefan's law. What are the units and dimensions of Stefan's cons...
Text Solution
|
- "Good reflectors are poor emitters of thermal radiation." explain.
Text Solution
|
- State Kirchhoff's law of radiations.
Text Solution
|
- What are the basic differences between , conduction, convection and ra...
Text Solution
|
- Distinguish between land breeze and sea breeze.
Text Solution
|
- The relation between principal specific heats of gases at constant pre...
Text Solution
|
- State Newton's law of cooling.
Text Solution
|