Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
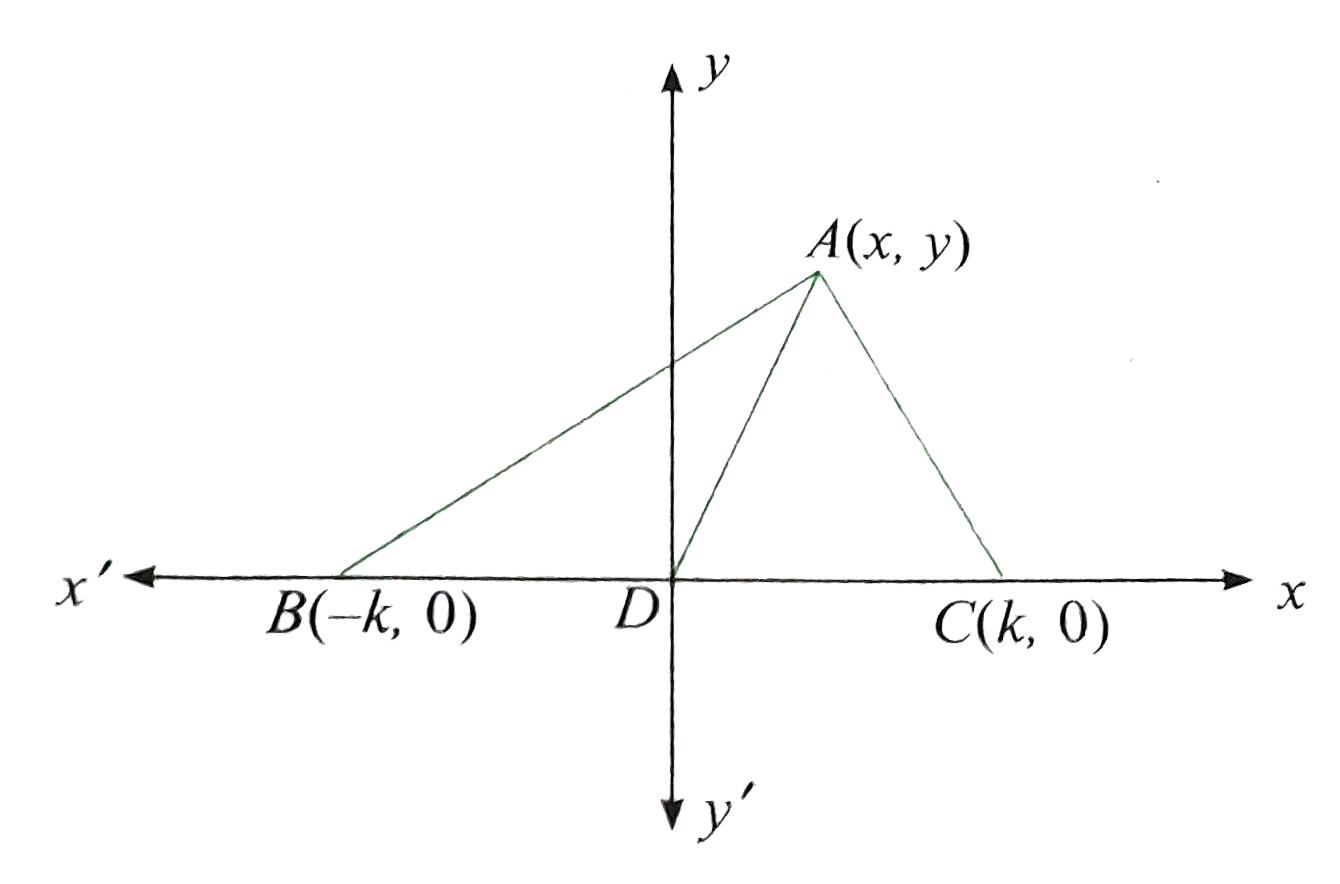
- In any triangle ABC, prove that AB^2 + AC^2 = 2(AD^2 + BD^2) , where D...
Text Solution
|
- ABC is a triangle in which AB=AC and D is a point on AC such that BC^(...
Text Solution
|
- A B C is a triangle in which A B=A C and D is any point in B C ....
Text Solution
|
- In an isoscles Delta ABC, AB= AC and D is a point on BC. Prove that AB...
Text Solution
|
- In Delta ABC, AB= AC. Side BC is produced to D. Prove that (AD^(2)-AC^...
Text Solution
|
- यदि DeltaABC की भुजा BC का मध्य बिन्दु D है तब सिद्ध कीजिये कि AB^(2...
Text Solution
|
- यदि DeltaABC की भुजा BC का मध्य बिन्दु D है तब सिद्ध कीजिये कि AB^(2...
Text Solution
|
- एक त्रिभुज ABC है | जिसमे AB = AC तथा D, BC पर कोई बिंदु है | तो सिद्ध...
Text Solution
|
- एक triangle ABC में, AB = AC तथा D, AC का मध्य बिंदु है और BC^(2) = AC...
Text Solution
|