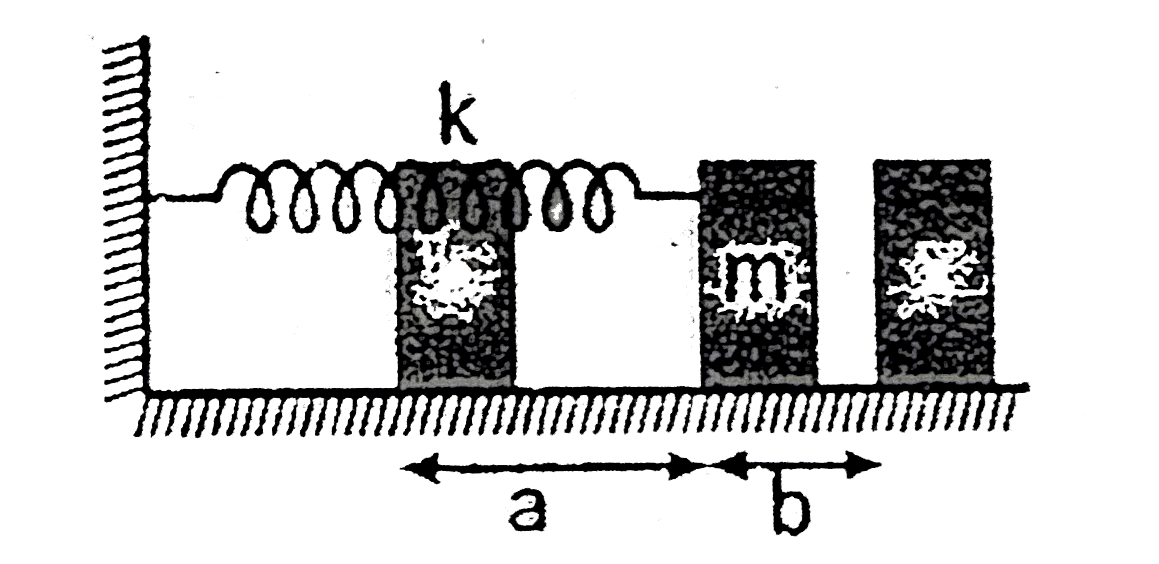Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- The spring is compressed by a distance a and released. The block again...
Text Solution
|
- The spring is compressed by a distance a and released. The block again...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is pushed up against a spring, compressing it a dist...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 8 kg is released from the top of an inclined smooth su...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass sqrt2 kg is released from the top of an inclined smoot...
Text Solution
|
- The block of mass m is released when the spring was in its natrual len...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 8 kg is released from the top of an inclined smooth su...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is released from rest onto a spring. A having stiffn...
Text Solution
|
- स्प्रिंग को a दुरी तक संपीडित करके छोड़ दिया जाता है ब्लॉक दुबारा तब स्...
Text Solution
|