A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
CENGAGE-AREA-Exercise (Multiple)
- Let A(k) be the area bounded by the curves y=x^2-3 and y=k x+2 The ra...
Text Solution
|
- The parabolas y^(2)=4x and x^(2)=4y divide the square region bounded b...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following have the same bounded area f(x)=s in x ,g(x)=s...
Text Solution
|
- If the curve y=ax^(1//2)+bx passes through the point (1,2) and lies ab...
Text Solution
|
- The area bounded by the curve x = a cos^3t,, y = a sin^3t, is :
Text Solution
|
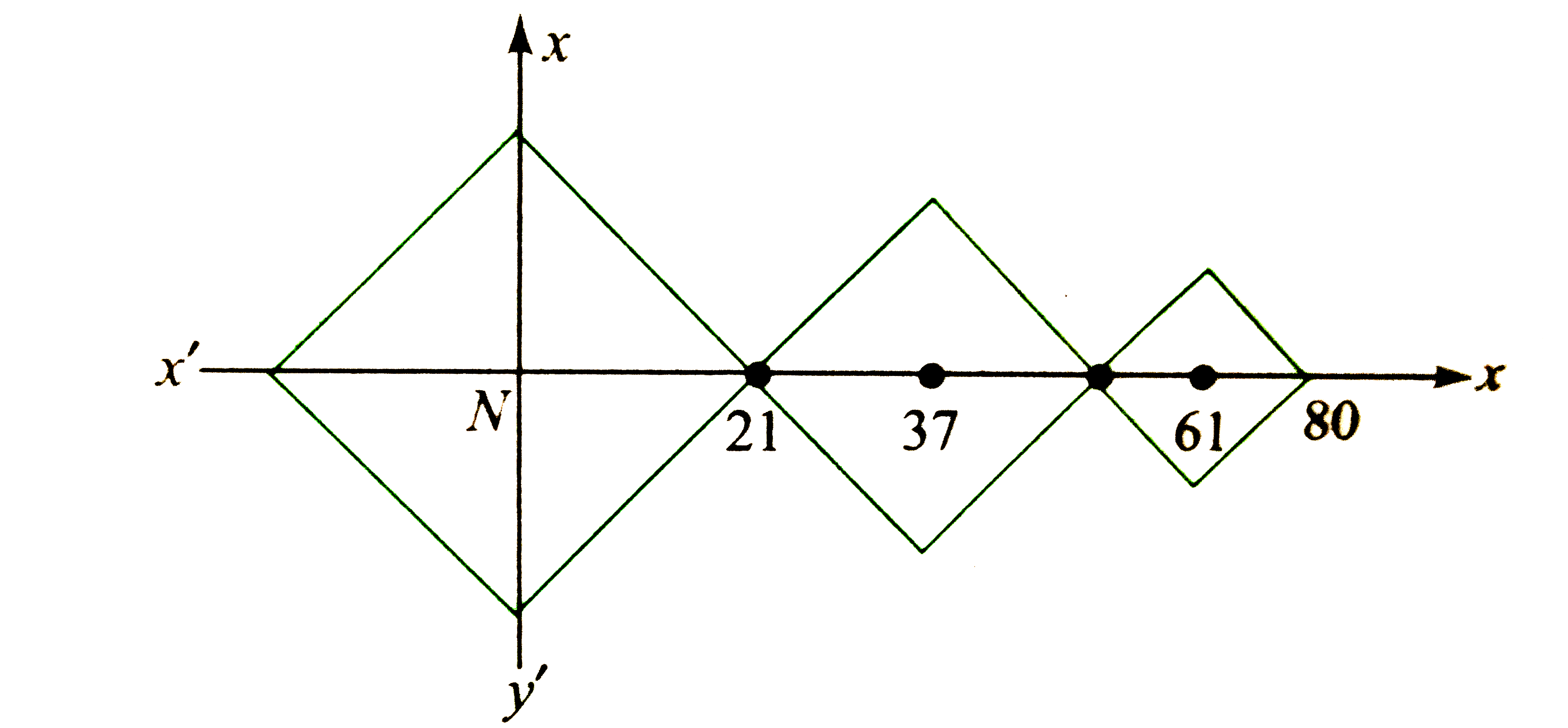
- If A1 is the area area bounded by |x-ai| + |y|=bi, i in N ,where a(i...
Text Solution
|
- The area of the region bounded by the curve y = 2x - x^2 and the line ...
Text Solution
|
- The area bounded by the curves y=|x|-1a n dy=-|x|+1 is 1 sq. units (b)...
Text Solution
|
- Consider curves S(1): sqrt(|x|)+sqrt(|y|)=sqrt(a), S(2): x^(2)+y^(2)=a...
Text Solution
|
- Let A(k) be the area bounded by the curves y=x^(2)+2x-3 and y=kx+1. Th...
Text Solution
|