Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FULL MARKS-SAMPLE PAPER-2 (SOLVED)-Part -IV
- Derive an expression for electrostatic potential due to an electric di...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the determination of the internal resistance of a cell using v...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the magnetic induction at a point on the axial line of a bar...
Text Solution
|
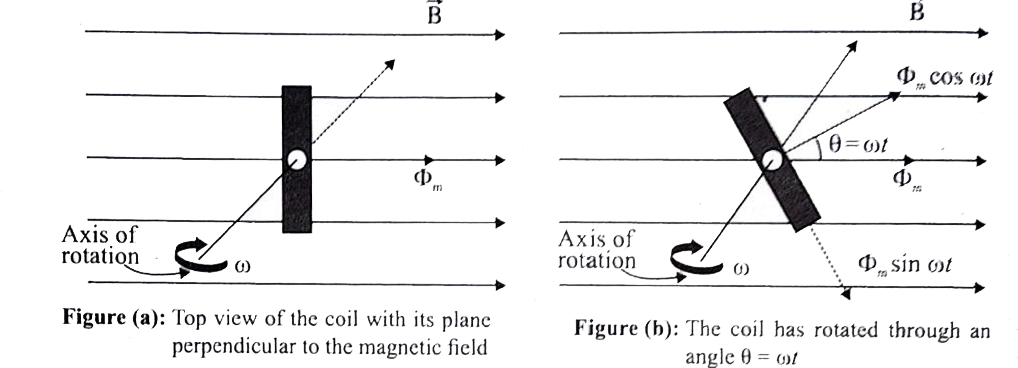
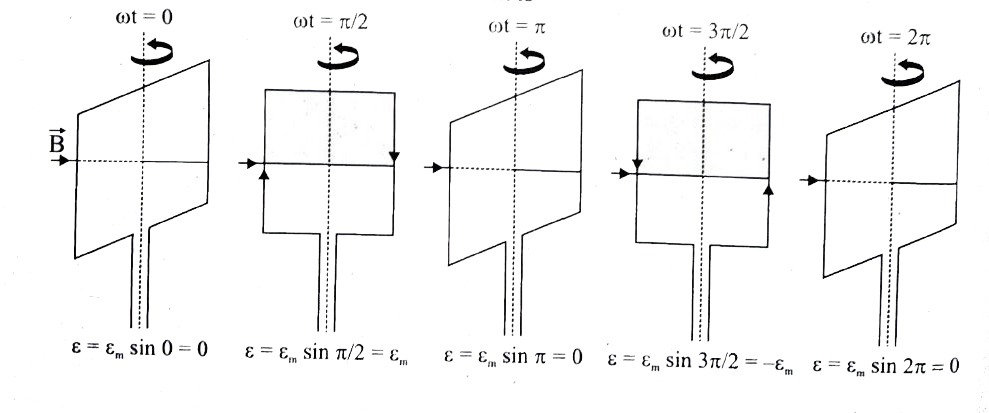
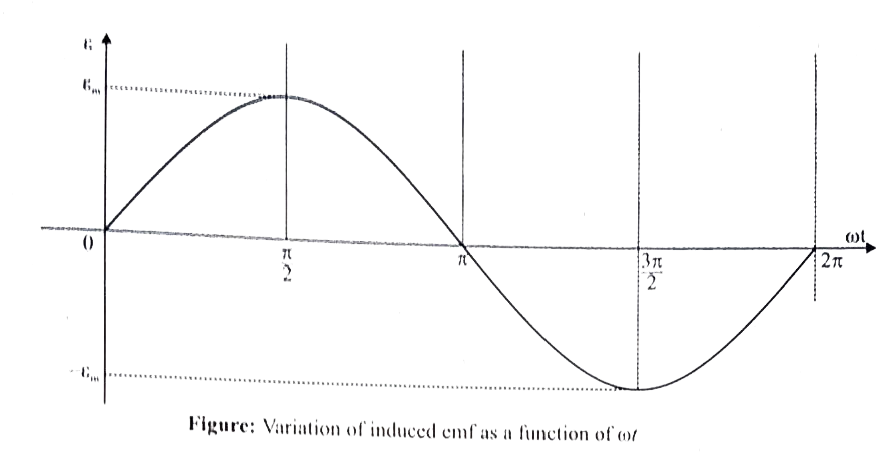
- Show mathematically that the rotation of a coll in a magnetic field ov...
Text Solution
|
- Write down the properties of electromagnetic waves.
Text Solution
|
- Derive the equation for acceptance angle and numerical aperture, of op...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the effect of potential difference on photoelectric current.
Text Solution
|
- Explain the J.J. Thomson experiment to determine the specific charge o...
Text Solution
|
- Draw the circuit diagram of a half wave rectifier and explain its work...
Text Solution
|
- Fiber optic communication is gaining popularity among the various tra...
Text Solution
|