To ensure the critical angle incidence in the core-cladding boundary inside the optical fibre, the light should be incident at a certain angle at the end of the optical fiber while entering in to it. This angle is called acceptance angle. It depends on the refractive indices of the cladding `n_(2)` and the outer medium `n_(3)`. Assume the light is incident at an angle called acceptance angle `i_a` at the outer medium and core boundary at A.
The Snell.s law in the product form, equation for this refraction at the point A.
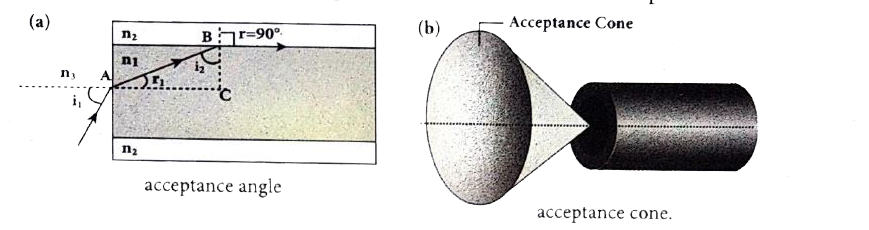
`n_(3) sin i_(a)=n_(1) sin r_(a)`
To have the total internal reflection inside optical fibre, the angle of incidence at the core-cladding interface at B should be atleast critical angle `i_c.` Snell.s law in the product form,equation for the refraction at point b is
`n_(1) sin i_(c)=n_(2) sin 90^(@)`
`n_(1) sin i_(c)=n_(2)" sin 90^(@)=1`
`sin i_(c)=n_(2)/n_(1)`
From the right angle `triangleABC`,
`i_(c)=90^(@)-r_(a)`
Now, equation (3) becomes, `sin (90^(@)-r_(a))=n_(2)/n_(1)`
Using trigonometry, `cos r_(a)=n_(2)/n_(1)`
Substituting for `cos r_(a)`
`sin r_(a)=sqrt(1-((n_(2))/(n_(1))^(2))=sqrt((n_(1)^(2)-n_(2)^(2))/(n_(1)^(2))) ..........(5)`
Substituting this in equation (1)
`n_(3) sin i_(a)=n_(1) sqrt((n_(1)^(2)-n_(2)^(2))/(n_(1)^(2)))=sqrt(n_(1)^(2)-n_(2)^(2)) .......(6)`
On further simplification,
`sin i_(a)= sqrt((n_(1)^(2)-n_(2)^(2))/(n_(3))) (or) sin i_(a)=sqrt((n_(1)^(2)-n_(2)^(2))/(n_(3)^(2))) .........(7)`
`i_(a)=sin^(-1) (sqrt((n_(1)^(2)-n_(2)^(2))/(n_(3)^(2))) .........(8)`
If outer medium is air, then `n_(3)=1`. The acceptance angle `i_(a)` becomes.
`i_(a)=sin^(-1) (sqrt(n_(1)^(2)-n_(2)^(2))` ...........(9)
Light can have any angle of incidence from 0 to `i_(a)` with the normal at the end of the optical fibre forming a conical shape called acceptance cone. In the equation (6), the term `(n_3 sin i_(a))` is called numerical aperture NA of the optical fibre.
`NA=n_(3) sin i_(a) (sqrt(n_(1)^(2)-n_(2)^(2)) .....(10)`
If outer medium is air, then `n_(3)=1`. The numberical aperture NA becomes,
`NA=sin i_(a)=sqrt(n_(1)^(2)-n_(2)^(2)) .......(11)`
