Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FULL MARKS-SAMPLE PAPER 9-PART-IV
- How do we determine the electric field due to a continuous charge dist...
Text Solution
|
- Obtain the macrscopic form of Ohm's law form its microscopic form and ...
Text Solution
|
- calculate the magnetic field inside and outside of the long solenoid u...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the construction and working of transformer.
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the source of electromagnetic waves
Text Solution
|
- Explain about compound mircoscope and obtain the equation for magnific...
Text Solution
|
- Write about electron microscope.
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the process of nuclear fission and its properties.
Text Solution
|
- Transistor functions as a switch. Explain.
Text Solution
|
- What is modulation? Explain the types of modulation with necessary dia...
Text Solution
|
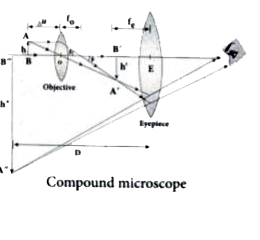 Magnification of compound microscope From the ray diagram, the linear magnification due to the objective is,
Magnification of compound microscope From the ray diagram, the linear magnification due to the objective is,