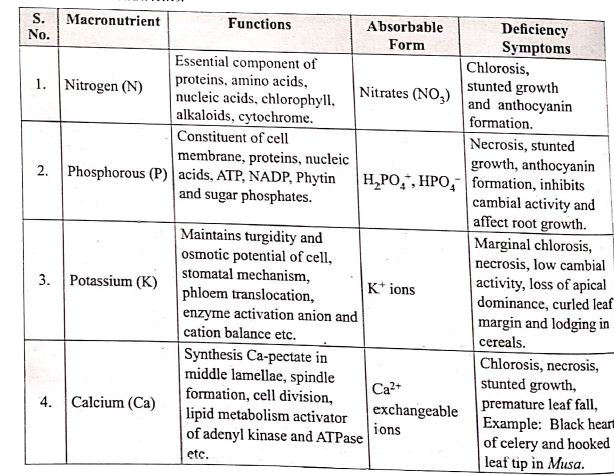
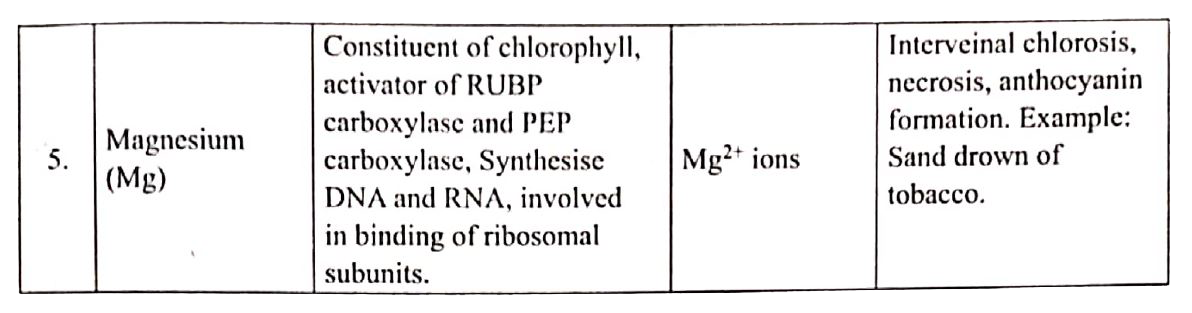
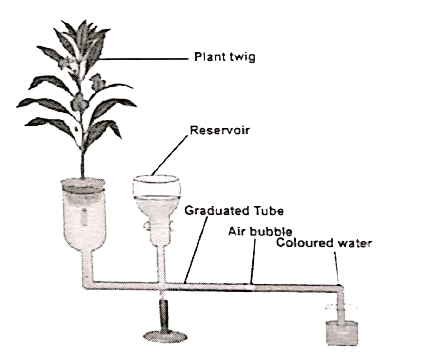
Ganongs potometer is used to measure the rate of transpiration indirectly. In this the amount of water absorbed is measured and assumed that this amount is equal to the amount of water transpired.
Apparatus consists of a horizontal graduated tube which is bent in opposite directions at the ends. one end is wide and the other is narrow. A reservoir is fixed to the horizontal tube near the wider end. the reservoir has a stopcock to regulate water flow. The apparatus is filled with water from reservoir . A twig or a small plant is fixed to the wider arm through a split cock. The other bent end of the horizontal tube is dipped into a beaker containing coloured water. an air bubble is introduced into the graduated tube at the narrow end kep this apparatus in bright sunlight and observe. As transpiration takes place, the air bobble will move towards the twig. the loss is compensated by water absorption through the xylem protion of the twig. Thus, the rate of water absorption is equal to the rate of transpiration.
OR