Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
TRANSPORT IN PLANTS
FULL MARKS|Exercise Additional Questions Solved (V). Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTs))|6 VideosTRANSPORT IN PLANTS
FULL MARKS|Exercise Additional Questions Solved (III. Short Answer Type Questions)|25 VideosTISSUE LEVEL OF ORGANISATION
FULL MARKS|Exercise ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS SOLVED (II. ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS)|17 VideosTRENDS IN ECONOMIC ZOOLOGY
FULL MARKS|Exercise Additional Questions Solved ( Answer the following questions.)|99 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FULL MARKS-TRANSPORT IN PLANTS -Additional Questions Solved (IV). Long Answer Type Questions)
- Write a note on carrier protein.
Text Solution
|
- Write a note on solute potneital.
Text Solution
|
- Name the possible routes for the path of water across root cells.
Text Solution
|
- Tabulate the difference between active absoprtion and passive absorpti...
Text Solution
|
- Explain about Cohesion - Tension Theory .
Text Solution
|
- What are the types of transpiration?
Text Solution
|
- Give an account on Starch - Sugar Interconversion Theory.
Text Solution
|
- Describe the K^(+) Transport theory on transpiration .
Text Solution
|
- Draw the structure of hydathode
Text Solution
|
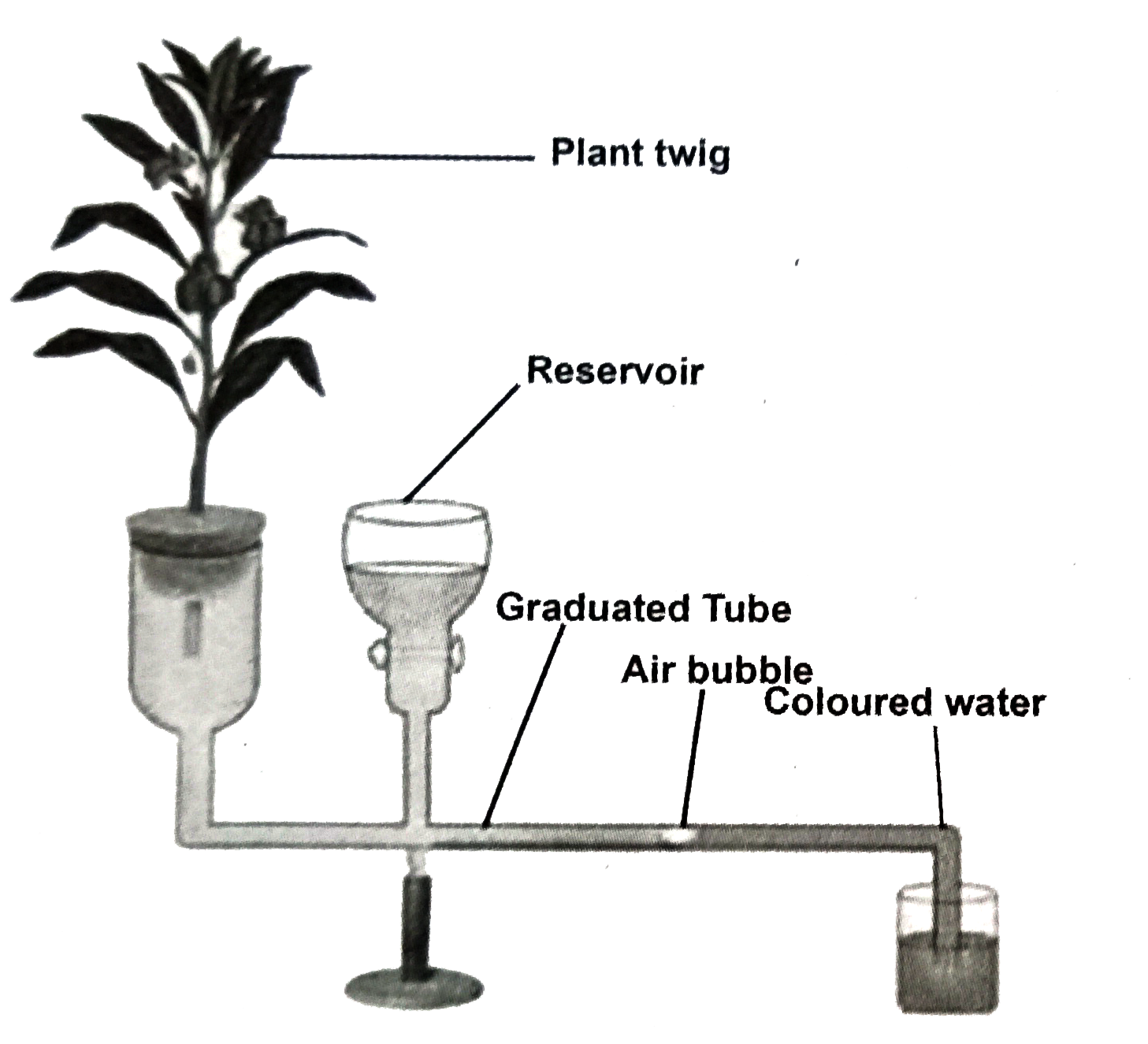
- Explain Ganong's Potometer experiment and its purpose.
Text Solution
|
- Describe ringing experiment with diagram.
Text Solution
|
- Write in detail about Passive Absorption of minerals salts.
Text Solution
|
- Describe Lundegardh's Cytochrome Pump Theory .
Text Solution
|
- Explain Protein - Lecithin Theory.
Text Solution
|