Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
MOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise Revision Exercises (Long Answer Questions )|12 VideosMOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise Revision Exercises (Numerical Problems )|18 VideosMOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise Revision Exercises (Fill in the Blanks )|10 VideosMAGNETISM AND MATTER
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER PRACTICE TEST FOR BOARD EXAMINATION|16 VideosNUCLEI
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER PRACTICE TEST FOR BOARD EXAMINATION|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MODERN PUBLICATION-MOVING CHARGES AND MAGNETISM-Revision Exercises (Short Answer Questions )
- A charged particle q is moving in the presence of a magnetic field B w...
Text Solution
|
- State the Biot-Savart law. Use it to obtain an expression for magnetic...
Text Solution
|
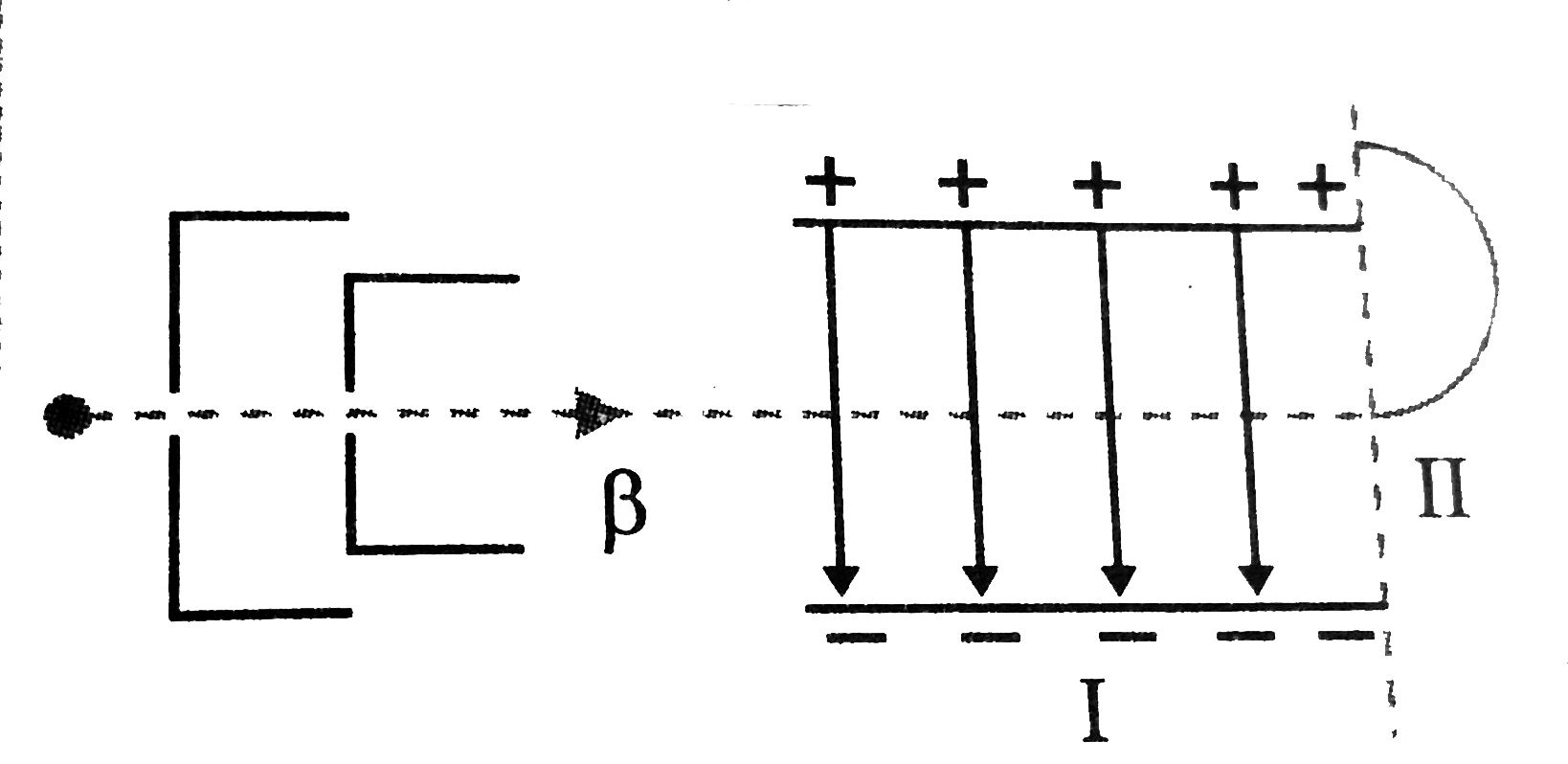
- A fine pencil of beta-particles, moving with a speed v, enters a regio...
Text Solution
|
- Two parallel wires carrying current in the same direction attract each...
Text Solution
|
- Explain the principle and working of a cyclotron with the help of a sc...
Text Solution
|
- A cyclotron is not suitable to accelerate electrons. Why?
Text Solution
|
- Using Biot-Savart’s law, derive an expression for magnetic field at an...
Text Solution
|
- A current I flows in a conductor placed perpendicular to the plate of ...
Text Solution
|
- Two small circular loops, marked (1) and (2), carrying equal currents ...
Text Solution
|
- A wire of length L is bent around in the form of a coil having N turns...
Text Solution
|
- Two identical coils P and Q each of radius R are lying in perpendicula...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular coil of sides l and b carrying a current I is subjected ...
Text Solution
|
- Define electric dipole moment. Is it a scalar or a vector? Derive the ...
Text Solution
|
- Increasing the current sensitivity of a galvanometer may not necessari...
Text Solution
|
- What is the function of the radial magnetic field in the moving coil g...
Text Solution
|
- Two protons P and Q moving with the same speed enter magnetic field B(...
Text Solution
|
- (a) How does a voltmeter differ from ammeter? (b) What is the main ...
Text Solution
|
- State Ampere's circuital law. By using it derive an expression for mag...
Text Solution
|
- (a) State the principle of working of a galvanometer. (b) Agalvanome...
Text Solution
|
- A galvanometer of resistance G can be converted into a voltmeter of ra...
Text Solution
|