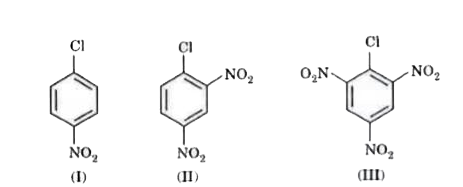
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise NCERT examplar Problems (Matching Type Questions)|6 VideosHALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise NCERT examplar Problems (Assertion and Reason Type Questions)|10 VideosHALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise NCERT examplar Problems (Multiple Choice Questions (Type-II))|12 VideosEQUILIBRIUM
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise Unit Practice Test|13 VideosHYDROCARBONS
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise UNIT PRACTICE TEST|15 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MODERN PUBLICATION-HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES-NCERT examplar Problems (Short Answer Type Questions)
- Out of o- and p-dibromobenzene which one has higher melting point and ...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the compounds will react faster in S(N)1 reaction with ""^(-)...
Text Solution
|
- Why iodoform has appreciable antiseptic property?
Text Solution
|
- Haloarenas are less reactive than haloalkanes and haloalkenes. Explain...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the role of Lewis acids in the preparation of aryl bromides an...
Text Solution
|
- Which of the following compounds (i) and (ii) will not react with a mi...
Text Solution
|
- Allyl chloride is hydrolysed more readily than n-propyl chloride. Why?
Text Solution
|
- Why is it necessary to avoid even traces of moisture during the use of...
Text Solution
|
- How do polar solvents help in the first step in S(N)1 mechanism ?
Text Solution
|
- Write a test to detect the presence of double bond in a molecule.
Text Solution
|
- Diphenyls are potential threat to the envioronment. How are these prod...
Text Solution
|
- What are the IUPAC names of the insecticide DDT and benzene hexachlori...
Text Solution
|
- Elimination reaction (especially beta - elimination) are as common as ...
Text Solution
|
- How will you obtain monobromobenzene from aniline ?
Text Solution
|
- Aryl halides are extremely less reactive towards nucleophilie substitu...
Text Solution
|
- tert-Butylbromide reacts with aq. NaOH by S(N)1 mechanism while n but...
Text Solution
|
- Predict the major product formed when HCl is added to isobutylene, Exp...
Text Solution
|
- Discuss the nature of C-X bond in the haloarenes.
Text Solution
|
- How can you obtain iodoethane from ethanol when no other iodine contai...
Text Solution
|
- Cyanide ion acts as an ambident nucleophille. From which end it acts a...
Text Solution
|