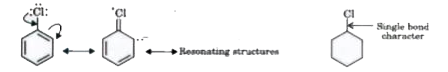Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise NCERT examplar Problems (Multiple Choice Questions (Type-I))|31 VideosHALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise NCERT examplar Problems (Multiple Choice Questions (Type-II))|12 VideosHALOALKANES AND HALOARENES
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise NCERT Textbooks Exercises|1 VideosGENERAL PRINCIPLES AND PROCESSES OF ISOLATION OF ELEMENTS
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise COMPETION FILE (Integer Type Numerical Value Type Questions)|5 VideosORGANIC COMPOUNDS CONTAINING NITROGEN
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise UNIT PRACTICE TEST|5 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MODERN PUBLICATION-HALOALKANES AND HALOARENES-NCERT Textbooks Exercise
- Write the structures of the following organic halogen compounds. (i)...
Text Solution
|
- Which one of the following has the highest dipole moment? (i) CH(2)C...
Text Solution
|
- A hydrocarbon C(5)H(10) does not react with chlorine in dark but gives...
Text Solution
|
- Write the isomers of the compound having formula C(4)H(9)Br.
Text Solution
|
- Write the equations for the preparation of 1-iodobutane from (i) 1-b...
Text Solution
|
- What are ambident nucleophiles? Explain with an example.
Text Solution
|
- Which compound in each of the following pairs will react faster in S(N...
Text Solution
|
- Predict all the alkenes that would be formed by dehydrohalogenation of...
Text Solution
|
- आप निम्नलिखित परिवर्तन कैसे करेंगे ? (i) Ethanol to but-1-yne (ii)...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why (i) the dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than tha...
Text Solution
|
- Give the uses of freon 12, DDT, carbon tetrachloride and iodoform.
Text Solution
|
- Write the structure of the major organic product in each of the follow...
Text Solution
|
- Write the mechanism of the following reaction: nBuBr + KCN overset(E...
Text Solution
|
- Arrange the compounds of each set in order of reactivity towards S(N)2...
Text Solution
|
- Out of C(6)H(5)CH(2)Cl and C(6)H(5)CHClC(6)H(5), which is more easily ...
Text Solution
|
- p-Dichlorobenzene has higher m.p. and solubility than those of -and m-...
Text Solution
|
- How the following conversions can be carried out? (i) Propene to pro...
Text Solution
|
- The treatment of alkyl chlorides with aqueous KOH leads to the formati...
Text Solution
|
- Primary alkyl halide C(4)H(9)Br (a) reacted with alcoholic KOH to give...
Text Solution
|
- What happens when (i) n-butyl chloride is treated with alcoholic KOH...
Text Solution
|