Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
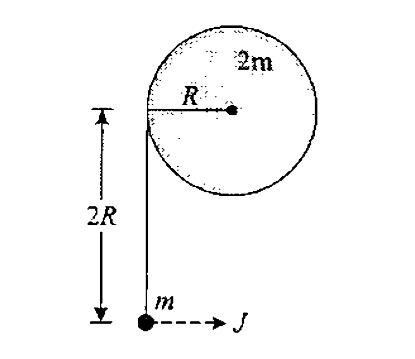
- A uniform circular disc of mass 2 m and radius R placed freely on a ho...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass m , radius R is placed on a smooth horizontal s...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of mass m and radius R lies flat on a smooth horizontal table. ...
Text Solution
|
- A smooth disc of mass M and radius (L)/(sqrt(3)) is placed at rest hor...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m strikes elastically with a disc of radius R, with...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform circular disc of mass 2 m and radius R placed freely on a ho...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass 'm' is attached to the rim of a uniform disc of mas...
Text Solution
|
- A disc of mass m and radius R is kept on a smooth horizontal surface w...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform disc of mass M and radius R is hinged at its centre C . A fo...
Text Solution
|