Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MBD -HARYANA BOARD-SOLUTIONS-LATQ ( LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS )
- What are ideal and non-ideal solutions ? What types of non-idealities ...
Text Solution
|
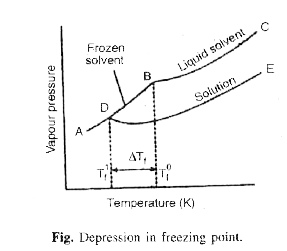
- Show graphically that the freezing point of a liquid will be depressed...
Text Solution
|
- Explain depression in freezing point. Show that it is a colligative pr...
Text Solution
|
- Define the following: (i) Boiling point (ii) Molal, depression con...
Text Solution
|
- Define osmosis and osmotic pressure and show that osmotic pressure is ...
Text Solution
|
- Why do we get sometimes abnormal molecular masses of the substances by...
Text Solution
|
- State Raoult's law. Why is the vapour pressure of a solvent lowered by...
Text Solution
|
- Commercially available conc. HCl contains 38% HCl by mass and has a de...
Text Solution
|
- Define boiling point and find out expression for the molecular mass of...
Text Solution
|
- What is meant by positive and negative deviation from Raoult's law and...
Text Solution
|
- Give any four characteristics of a non-ideal solution showing positive...
Text Solution
|
- What are important characteristics of a non-ideal solution showing neg...
Text Solution
|
- At 298 K, 100 ml solution containing 3.002 g of solute gave an osmotic...
Text Solution
|
- Why is osmotic pressure technique preferred over other methods to find...
Text Solution
|
- Boiling point of water at 750 mm is 99.63^@ C. How much of sucrose is ...
Text Solution
|
- The boiling point of water (100^@ C) becomes, 100.52^@ C if 3 g of non...
Text Solution
|
- 27.75 g of CaCl2, dissolved in 250 ml of solutions. Find molarity of c...
Text Solution
|
- State Raoult's law for solutions containing non-volatile solutes in vo...
Text Solution
|
- Derive Raoult's law for non-volatile solutes.
Text Solution
|
- Mention three characteristics of ideal solutions. What cause deviation...
Text Solution
|