Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
ELECTROCHEMISTRY
MBD -HARYANA BOARD|Exercise LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS|12 VideosELECTROCHEMISTRY
MBD -HARYANA BOARD|Exercise VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS|12 VideosCHEMISTRY IN EVERYDAY LIFE
MBD -HARYANA BOARD|Exercise Long answer type questions|5 VideosGENERAL PRINCIPLES AND PROCESSES OF ISOLATION OF ELEMENTS
MBD -HARYANA BOARD|Exercise LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MBD -HARYANA BOARD-ELECTROCHEMISTRY-SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
- Calculate standard Gibbs free energy for the reaction : Zn+Cu^(2+)toZn...
Text Solution
|
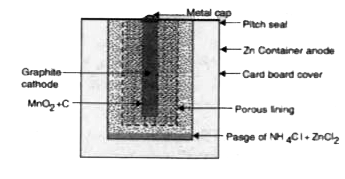
- What is a primary cell ? Describe the construction and working of dry ...
Text Solution
|
- While giving labelled diagram of dry cell write reactions taking place...
Text Solution
|
- How much electricity in terms of Faraday is required to produce (i) ...
Text Solution
|
- Define molar conductance and secondary cells.
Text Solution
|
- Define equivalent conductance and primary cells.
Text Solution
|
- State and explain Kohlrausch's law. How does it help in the calculatio...
Text Solution
|
- Define the processes of oxidation and reduction with example.
Text Solution
|
- How an electrochemical cell is represented by cell notation ?
Text Solution
|
- Explain why blue colour of CuSO(4) solution is discharged when Zn rod ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the standard Gibbs free energy (DeltaG^(@)) for the given reactio...
Text Solution
|
- What is a fuel cell ? Give advantages of a fuel cell.
Text Solution
|
- If a current of 0.5 ampere flows through a metallic wire for 2 hours, ...
Text Solution
|
- How many coulombs are required to produce 40.5 g of Al from molten Al(...
Text Solution
|
- Why does the conductivity of a solution decrease with dilution ?
Text Solution
|
- What are two functions of Salt bridge in an Electrochemical cell ?
Text Solution
|
- List the important uses of salt bridge.
Text Solution
|
- What is sacrificial protection from rusting ? Which metal is generally...
Text Solution
|
- 0.05 M NaOH solution offered a resistance of 31.6 ohm in a conductivit...
Text Solution
|
- What is corrosion ? What are the factors which affect corrosion ?
Text Solution
|