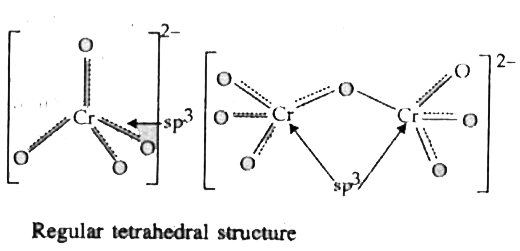
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MBD -HARYANA BOARD-THE D- AND F- BLOCK ELEMENTS-LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
- How would you account for the following: (a) of the d^(4) species, ...
Text Solution
|
- Describe the preparation of potassium permanganate from pyrolusite ore...
Text Solution
|
- Describe the preparation of potassium permanganate. How does the acidi...
Text Solution
|
- How does acidified KMnO solution react with the following: (i) FeSO...
Text Solution
|
- Explain with chemical reactions three oxidising properties of KMnO(4) ...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Write ionic equations for the reaction of acidified potassium perm...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Why are Mn^(2+) compounds more stable than Fe^(2+) towards oxidati...
Text Solution
|
- (a) How is potassium dichromate prepared from chromite ? How does it r...
Text Solution
|