Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
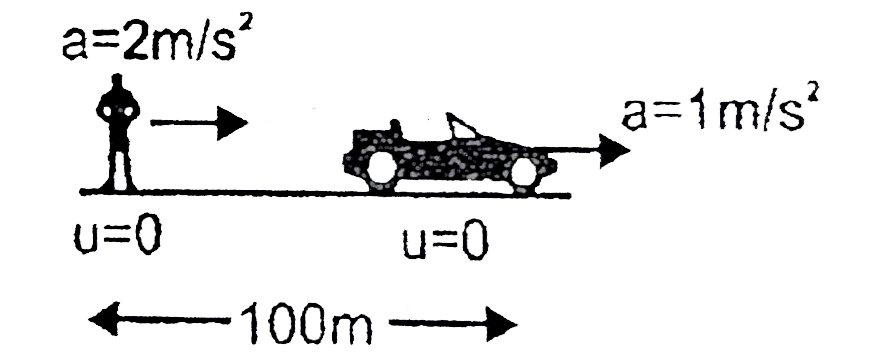
- Initially a man and a car both are stationary and situated at a distan...
Text Solution
|
- A man of mass m is standing on a stationary flat car of mass M. The ca...
Text Solution
|
- Initially car A is 10.5 m ahead of car B . Both start moving at time t...
Text Solution
|
- Two cars A and B moving on two straight tracks inclined at an angle 60...
Text Solution
|
- Initially a man and a car both are stationary and situated at a distan...
Text Solution
|
- दो स्थानों 'A' तथा 'B' के बीच की दूरी 70 किमी है । दो कारे एक ही समय च...
Text Solution
|
- A और B बिंदु राजमार्ग पर 100 किमी. दूरी पर है । एक कार A से और दूसरी क...
Text Solution
|
- दो स्थानों A और B के बीच कि दूरी 60 कि. मी. है । दो कारे एक ही समय में...
Text Solution
|
- एक राजमार्ग पर दो स्थान A और B, 100 किमी की दूरी पर है । एक कार A से त...
Text Solution
|