Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
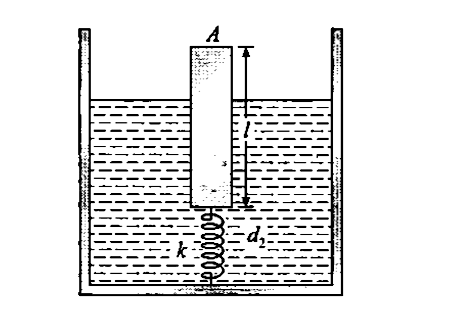
- A uniform cylindrical block of length l density d(1) and area of cross...
Text Solution
|
- Let d(1),d(2),d(3),......,d(k) be all the divisors of a positive integ...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement as shown, A and B arc two cylinders each of length ...
Text Solution
|
- A body of density d(2) is dropped from rest at a height x into a beake...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform cylindrical block of length l density d(1) and area of cross...
Text Solution
|
- Two cylinders of same cross-section and length L but made of two diffe...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder of mass M and density d(1) hanging from a string, is lowere...
Text Solution
|
- An object weights m(1) in a liquid of density d(1) and that in liquid ...
Text Solution
|
- A small body with relative density d(1) falls in air from a height 'h'...
Text Solution
|