Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
COLLISION
FIITJEE|Exercise ASSIGNMENT PROBLEMS (SUBJECTIVE) Level - I (Short Answer Type Questions)|2 VideosCOLLISION
FIITJEE|Exercise ASSIGNMENT PROBLEMS (SUBJECTIVE) Level - I (Fill in the blanks)|3 VideosCOLLISION
FIITJEE|Exercise SOLVED PROBLEMS (OBJECTIVE) MATRIX MATCH TYPE|2 VideosAC CIRCUITS
FIITJEE|Exercise ASSERTION REASONING TYPE|1 VideosCURRENT ELECTRICITY
FIITJEE|Exercise Comprehension -4|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
FIITJEE-COLLISION -Exercise
- Centre of mass is at point X (1,1,1) when system consists of particles...
Text Solution
|
- Particle of masses 2 kg, 2 kg, 1 kg and 1 kg are placed at the corners...
Text Solution
|
- Linear mass density of a rod PQ of length l and mass m is varying with...
Text Solution
|
- Find the location of centre of mass of a uniform semicircular plate of...
Text Solution
|
- Determine the centre of mass of a uniform hemisphere of radius R.
Text Solution
|
- A thin homogeneous lamina is in the form of a circular disc of radius ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the centre of mass of the section. Consider the mass of the lamin...
Text Solution
|
- Can a sailboat be propelled by air blown at the sails from a fan attac...
Text Solution
|
- (i) Find the acceleration of the centre of mass of two particle appro...
Text Solution
|
- A body when thrown upwards, changes its velocity therefore it changes ...
Text Solution
|
- A gun is mounted on a stationary rail road car. The mass of the car, t...
Text Solution
|
- A man of mass m climbs a rope of length L suspended below a balloon of...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass 50 gm is dropped from a height h = 10 m. It rebounds lo...
Text Solution
|
- The area of F.t curve is A. If one of the colliding bodies of mass m i...
Text Solution
|
- Two blocks of masses m and 3m are connected by an inextensible string ...
Text Solution
|
- A bullet of mass m strikes a block of mass M connected to a light spri...
Text Solution
|
- Two block of mass 2 kg and M kg are at rest on an inclined plane and a...
Text Solution
|
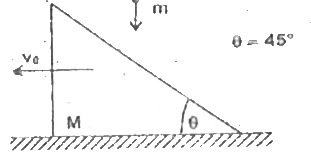
- A triangular wedge of mass M is moving with uniform velocity v(0) alon...
Text Solution
|
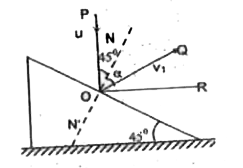
- An iron ball A collides with another stationary iron ball B If the rat...
Text Solution
|
- Two bodies A and B of masses m and 2m respectively are placed on a sm...
Text Solution
|