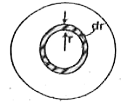
Choose a circular path centred on the axis of the conductor and apply Ampere.s law
(a) To find the current passing through the area enclosed by the path integrate
`dI = jdA = (kr^(2)) (2 pi r dr)`
`implies I = int dI = K int_(0)^(r) 2 pi r^(2) dr = (k pi r^(4))/(2)`
since `int vec(B) .d vec(l) = mu_(0) I`
`implies B2 pi r = mu_(0) . (pi k r^(4))/(2) implies B = (mu_(0) kr^(3))/(4)`
(b) If r > a then net current through the Amperian loop is
`I = int_(0)^(a) 2 pi r dr = (pi Ka^(4))/(2)`
`implies B = (mu_(0) Ka^(4))/(4r)`