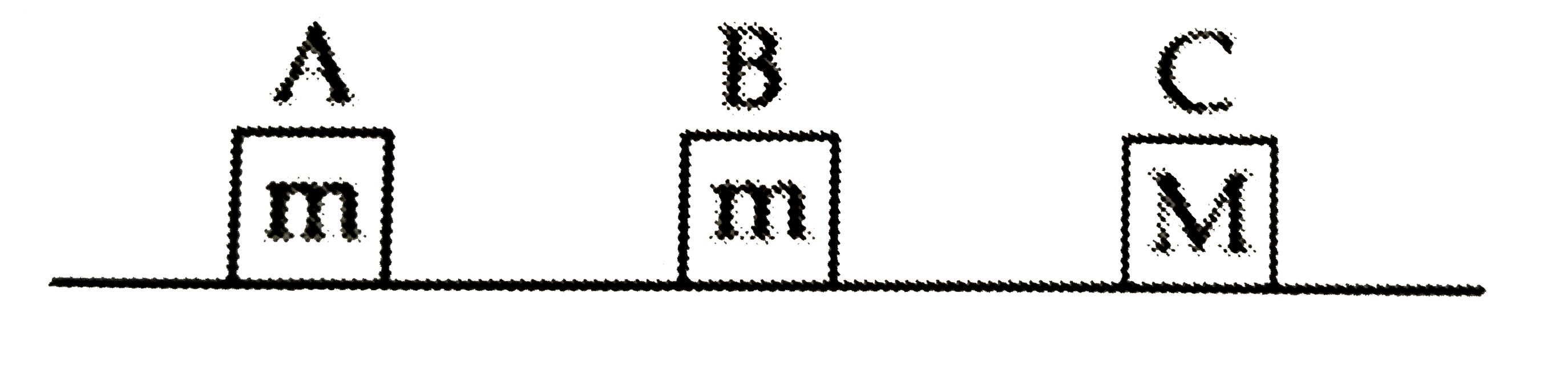A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
WORK, ENERGY AND POWER
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise Objective Type Questions (JEE (Advanced) for IIT Entrance)|7 VideosWORK, ENERGY AND POWER
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise Objective Type Questions (C. Multiple Choice Questions)|16 VideosWORK, ENERGY AND POWER
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise Objective Type Questions (B. Multiple Choice Questions)|46 VideosWAVES
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER PRACTICE TEST|14 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MODERN PUBLICATION-WORK, ENERGY AND POWER -Objective Type Questions (JEE (Main) & Other State Boards for Engineering Entrance)
- The block of mass M moving on the frictionless horizontal surface col...
Text Solution
|
- An oscillator of mass M is at rest in its equilibrium position in a po...
Text Solution
|
- Three blocks A, B and C are lying on a smooth horizontal surface, as s...
Text Solution
|
- A ball of mass 0.2 kg is thrown vertically upwards by applying a force...
Text Solution
|
- A locomotive of mass m starts moving so that its velocity varies accor...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m, lying on a smooth horizontal surface, is attached t...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 0.50 kg is moving with a speed of 2.00 m/s on a smoot...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is moving in a circular path of radius a under the action o...
Text Solution
|
- A spherical ball of mass 20kg is stationary at the top of a hill of he...
Text Solution
|
- A force acts on a 2 kg object so that its position is given as a funct...
Text Solution
|
- At time t=0s particle starts moving along the x- axis. If its kinetic ...
Text Solution
|
- When a rubber-band is stretched by a distance x, it exerts a restoring...
Text Solution
|
- A particle of mass m moving in the x direction with speed 2v is hit by...
Text Solution
|
- A mass m moves with a velocity v and collides inelastically with anoth...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m=0.1 kg is connceted to a spring of unknown spring co...
Text Solution
|
- Three masses m , 2m and 3m are moving in X-Y plane with speed 3u , 2...
Text Solution
|
- The upper half of an inclined plane with inclination phi is perfectly ...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 'm' is connected to another block of mass 'M' by a spr...
Text Solution
|
- A mass of M kg is suspended by a weightless string. The horizontal for...
Text Solution
|
- A point particle of mass m, moves long the uniformly rough track PQR a...
Text Solution
|