Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER PRACTICE TEST|14 VideosRAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS (MATRIX MATCH TYPE QUESTIONS)|1 VideosNUCLEI
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER PRACTICE TEST FOR BOARD EXAMINATION|15 VideosSEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS METERIALS DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise CHAPTER PRACTICE TEST FOR BOARD EXAMINATION|12 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MODERN PUBLICATION-RAY OPTICS AND OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS-OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS (INTEGER TYPE QUESTIONS)
- There is a concave mirror of focal length f and an object of length 2....
Text Solution
|
- When some object is kept at a distances u(1) and u(2) from the concave...
Text Solution
|
- A layer of oil 3 cm thick is floating on a layer of coloured water 5 c...
Text Solution
|
- Magnification of simple microscope is found to be 3 when image is form...
Text Solution
|
- R is the radius of curvature for both the surfaces of lens shown in fi...
Text Solution
|
- A person wants to use +20 D lens as simple microscope. If the person u...
Text Solution
|
- Sunlight of intensity 1.3kW m^(–2) is incident normally on a thin conv...
Text Solution
|
- There is a concave mirror of radius of curvature 20cm. A point object ...
Text Solution
|
- A convex lens is made of three different materials which are symmetric...
Text Solution
|
- A prism is shown in the figure with prism angle 75^(@) and refractive ...
Text Solution
|
- Consider a concave mirror and a convex lens (refractive index 1.5) of ...
Text Solution
|
- A monochromatic beam of light is incident at 60^@ on one face of an eq...
Text Solution
|
- A monochromatic light is travelling in a medium of refractive index n ...
Text Solution
|
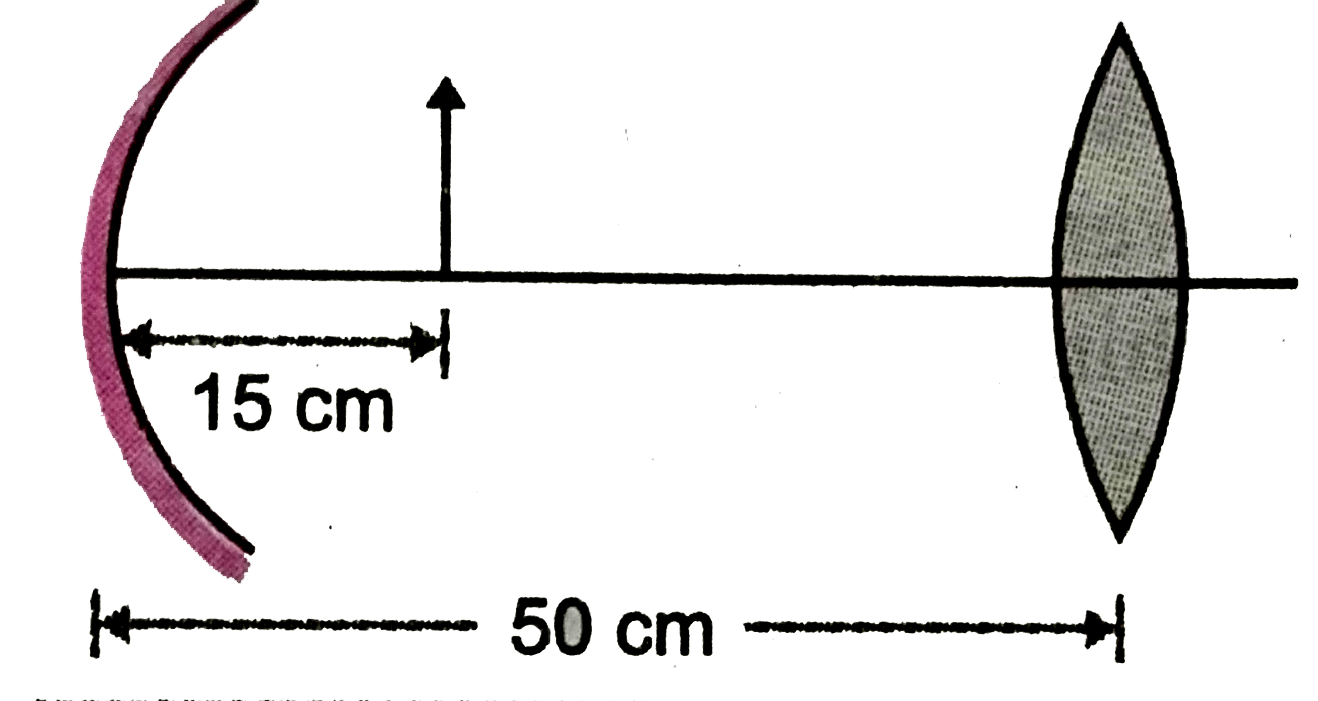 .
.