Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
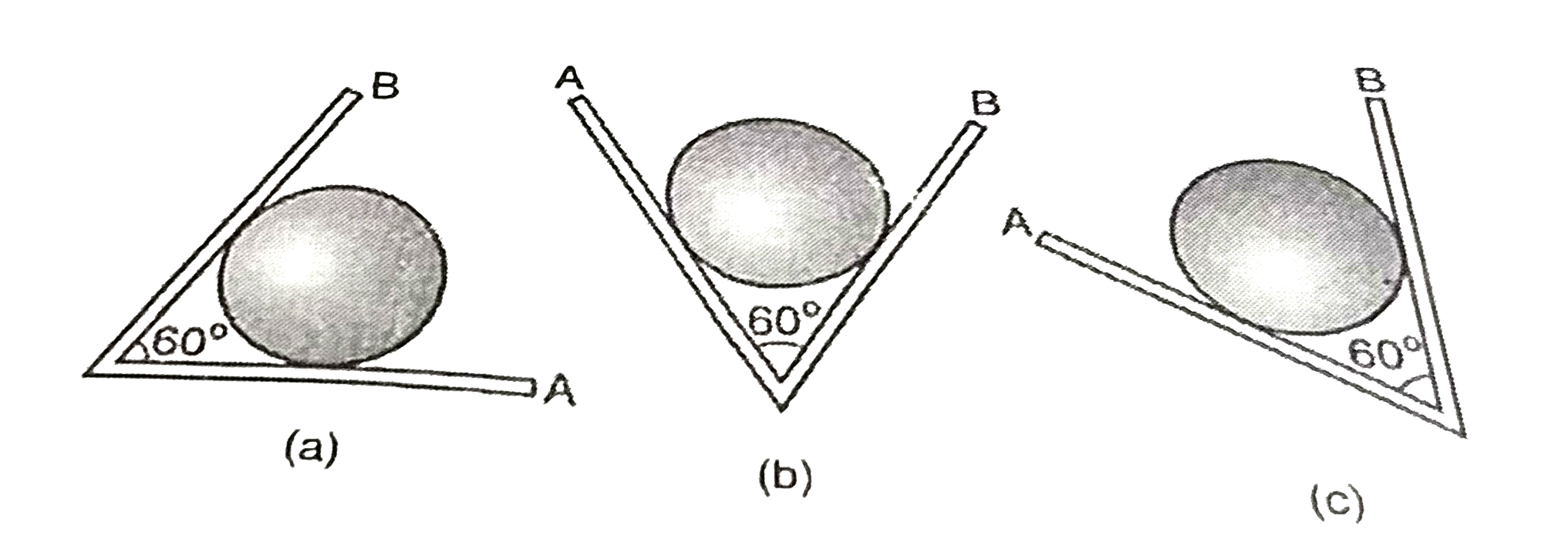
- An iron sphere weights 10 N and rests in a V- shaped trough whose side...
Text Solution
|
- A rod AB of weight w(1) is placed over a sphere of weight w(2) shown i...
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere of mass 2 kg is resting inside a cube as shown in fig. ...
Text Solution
|
- An iron sphere weighing 10N rests in a V shaped smooth trough whose si...
Text Solution
|
- A metal sphere is hung by a string fixed to a wall. The forces acting ...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere strikes a wall and rebounds with coefficient of restitution (...
Text Solution
|
- A sphere is rotatiing between a a rough wall and a smooth wedge as sho...
Text Solution
|
- An iron sphere weights 10 N and rests in a V- shaped trough whose side...
Text Solution
|
- A metal sphere is hung by a string fixed to a wall. The forces acting ...
Text Solution
|