Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
HYDROSTATICE
PEARSON IIT JEE FOUNDATION|Exercise LEVEL 2 UNDERSTANDING BASED QUESTION|6 VideosHYDROSTATICE
PEARSON IIT JEE FOUNDATION|Exercise LEVEL 3|5 VideosHYDROSTATICE
PEARSON IIT JEE FOUNDATION|Exercise LEVEL 1 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS|29 VideosHEAT
PEARSON IIT JEE FOUNDATION|Exercise All Questions|115 VideosLIGHT
PEARSON IIT JEE FOUNDATION|Exercise Level 3|10 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
PEARSON IIT JEE FOUNDATION-HYDROSTATICE-LEVEL 2
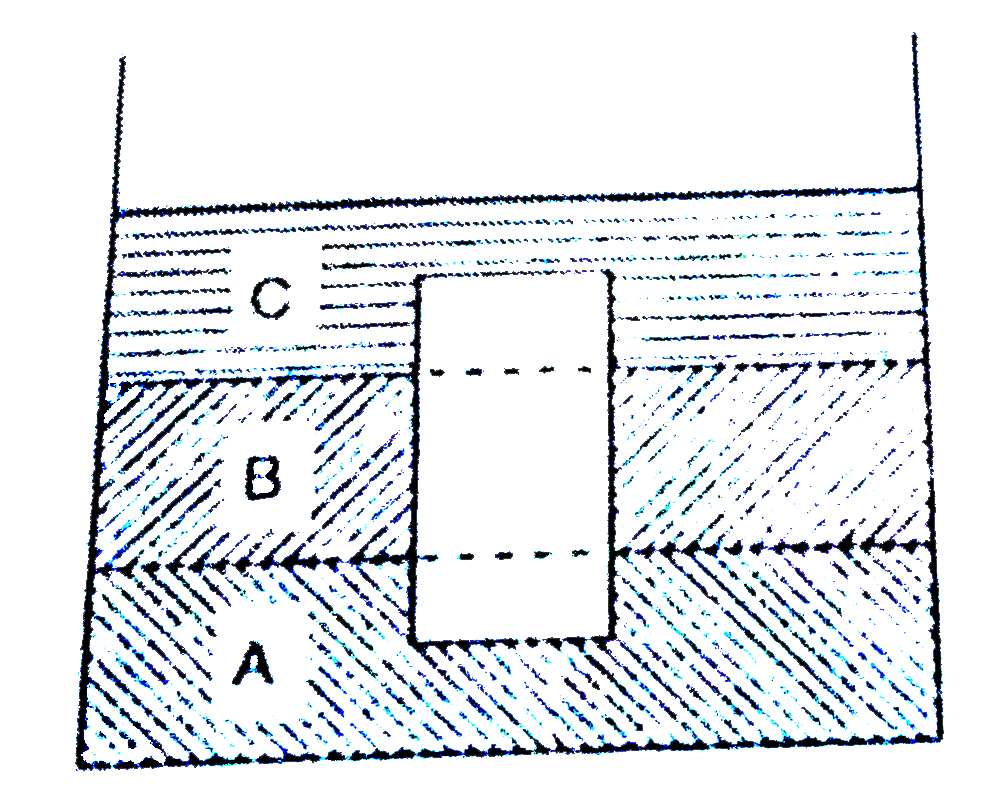
- An object floats in three immiscible liquids A, B and C of densities 3...
Text Solution
|
- A hollow sphere of external and internal diameter 4 cm and 2 cm, respe...
Text Solution
|
- Two sphere S(1)andS(2) made of the same material and having radii 2r a...
Text Solution
|
- A simple barometer tube contains some air in it. The length of the tub...
Text Solution
|
- A 'U' tube contains oil, carbon tetrachloride and water as shown in th...
Text Solution
|
- A metallic sphere is made of an alloy of metels 'P' and 'Q' having spe...
Text Solution
|
- A trough contains the two immiscible liquids 'A' and 'B' having densit...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown below, cylinder A has pump piston, whereas B and C...
Text Solution
|
- An empty glass test tube floats vertically in water to a depth of 5 cm...
Text Solution
|
- Two metallic spheres 'P' and 'Q' weighing 200 gwt and 150 gwt, respect...
Text Solution
|
- A gold ornament weighs 570 gram in air nad 520 gram in water. If the s...
Text Solution
|
- A container is filled with two immiscible liquids A and B of densities...
Text Solution
|
- A variable immersion hydrometer is used to measure the specific gravit...
Text Solution
|