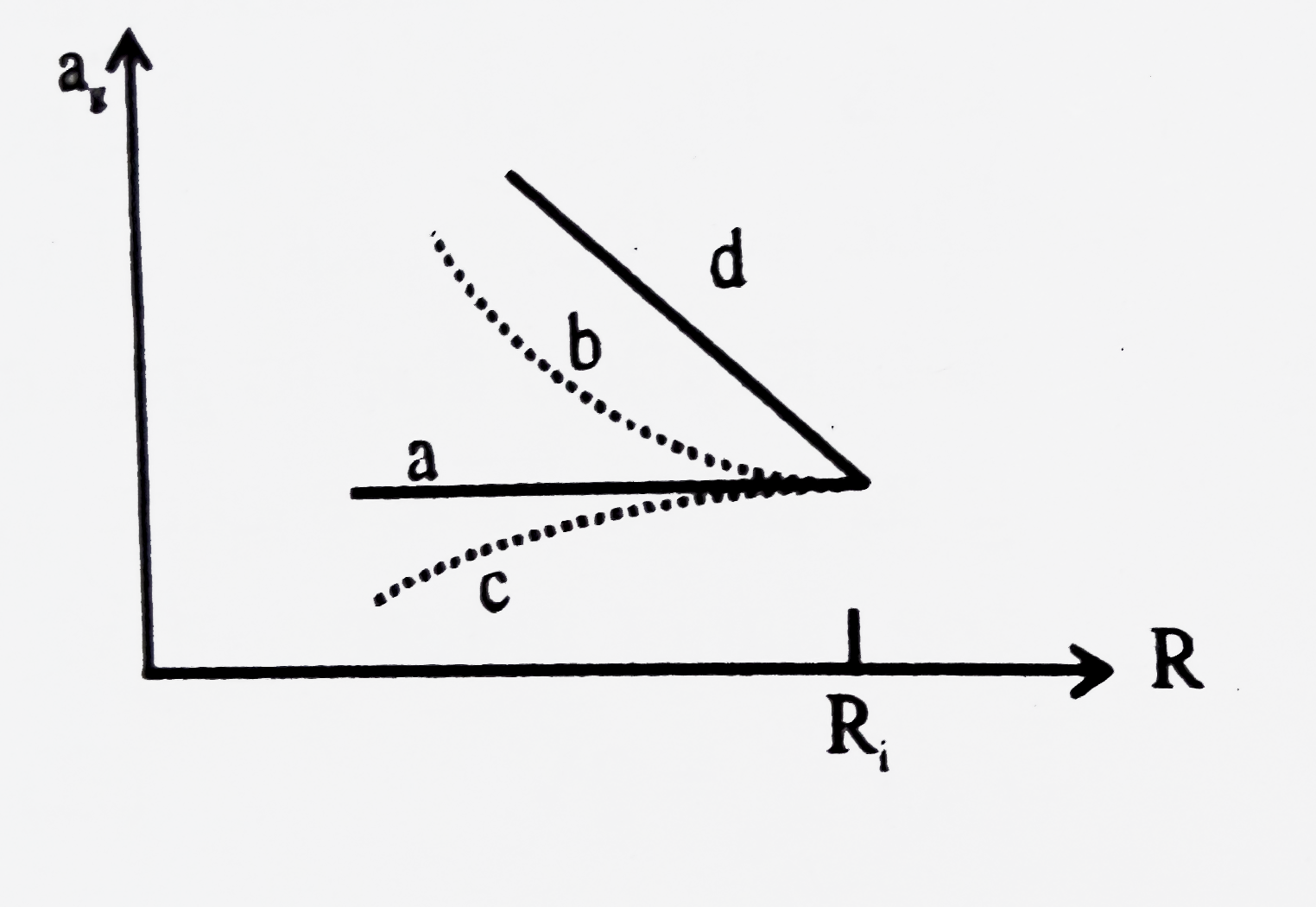
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GRAVITATION
DISHA PUBLICATION|Exercise EXERCISE-2|30 VideosGRAVITATION
DISHA PUBLICATION|Exercise EXERCISE-2|30 VideosELECTROSTATIC POTENTIAL AND CAPACITANCE
DISHA PUBLICATION|Exercise EXERCISE 2: CONCEPT APPLICATOR|24 VideosJEE MAINS- 2019 (HELD ON :9TH APRIL 2019 (SHIFT-I))
DISHA PUBLICATION|Exercise QUESTIONS|30 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
DISHA PUBLICATION-GRAVITATION-EXERCISE -1
- Let omega be the angular velocity of the earth's rotation about its ax...
Text Solution
|
- If earth is supposed to be a sphere of radius R , if g(30) is value of...
Text Solution
|
- A(nonrotating) star collaps onto from an initial radius R(i) with its ...
Text Solution
|
- If the mass of earth is eighty times the mass of a planet and diameter...
Text Solution
|
- A research satellite of mass 200 kg circles the earth in an orbit of a...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows variation of acceleration due to gravity with distance fr...
Text Solution
|
- The acceleration due to gravity on the planet A is 9 times the acceler...
Text Solution
|
- A roller coaster is designed such that riders experience "weightlessne...
Text Solution
|
- In a certain region of space gravitational field is given by I = - (k/...
Text Solution
|
- Gravitational field intensity at the centre of the semi circle formed ...
Text Solution
|
- A planet is moving in an elliptic orbit. If T,V,E and L stand, respect...
Text Solution
|
- If g is the acceleration due to gravity on the earth's surface, the ga...
Text Solution
|
- The magnitude of gravitational potential energy of the moon earth sys...
Text Solution
|
- The gravitational potential due to earth at infinite distance from it ...
Text Solution
|
- Two rings having masses M and 2M respectively, having the same radius ...
Text Solution
|
- The escape velocity of an object projected from the surface of a given...
Text Solution
|
- The mean radius of earth is R, its angular speed on its own axis is w ...
Text Solution
|
- The moon has a mass of (1)/(81) that of the earth and radius of (1)/(...
Text Solution
|
- A planet in a distant solar systyem is 10 times more massive than the ...
Text Solution
|
- What is the minimum energy required to launch a satellite of mass m fr...
Text Solution
|