Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
OSCILLATIONS
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise Practice Questions|57 VideosOSCILLATIONS
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise Checkpoint|8 VideosMOTION IN TWO AND THREE DIMENSIONS
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise PRACTICE QUESTIONS (MATRIX-MATCH)|10 VideosPHOTONS AND MATTER WAVES
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise PRACTICE QUESTIONS(Integer Type)|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY-OSCILLATIONS-Problems
- A 10g particle undergoes SHM with an amplitude of 2.0mm, a maximum acc...
Text Solution
|
- Figure 15.32a is a partial graph of the position function x(t) for a s...
Text Solution
|
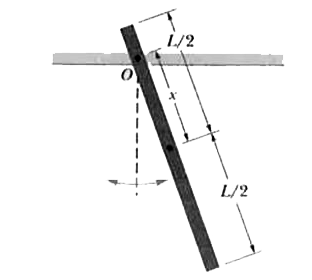
- In Fig. 15.33, a stick of length L= 1.65 m oscillates as a physical pe...
Text Solution
|
- What is the phase constant for the harmonic oscillator with the veloci...
Text Solution
|
- What is the oscillation amplitude of a 4.00kg box oscillating on a spr...
Text Solution
|
- A 5.00kg object on a horizontal frictionless surface is attached to a ...
Text Solution
|
- What is the maximum acceleration of a platform that oscillates at ampl...
Text Solution
|
- What is the phase constant for the harmonic oscillator with the positi...
Text Solution
|
- A body undergoes simple harmonic motion of amplitude 4.25cm and period...
Text Solution
|
- A thin uniform rod (mass= 0.90kg) swings about an axis that passes thr...
Text Solution
|
- A pendulum is formed by pivoting a long thin rod about a point on the ...
Text Solution
|
- The 0.800kg cube in Fig. 15.38 has edge lengths d= 6.00cm and is mount...
Text Solution
|
- Figure 15.39 shows the kinetic energy K of a simple harmonic oscillato...
Text Solution
|
- An object undergoing simple harmonic motion takes 0.25g to travel from...
Text Solution
|
- If the phase angle for a block -spring system in SHM is pi//8 rad and ...
Text Solution
|
- An oscillator consists of a block attached to a spring (k= 425N/m). At...
Text Solution
|
- An oscillating block-spring system takes 0.25s to begin repeating its ...
Text Solution
|
- A particle with a mass of 3.00 xx 10^(-20)kg is oscillating with simpl...
Text Solution
|
- When the displacement in SHM is 0.40 times the amplitude x(m), what fr...
Text Solution
|
- A block rides on a piston (a squatcylindrical piece) that is moving ve...
Text Solution
|