Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
GAUSS' LAW
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise CHECKPOINT|7 VideosGAUSS' LAW
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise PROBLEMS|42 VideosFORCE AND MOTION-II
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise PRACTICE QUESTIONS (Integer Type)|1 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS : REFLECTION
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise PRACTICE QUESTIONS (Integer Type)|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY-GAUSS' LAW -PRACTICE QUESTIONS (INTEGER TYPE)
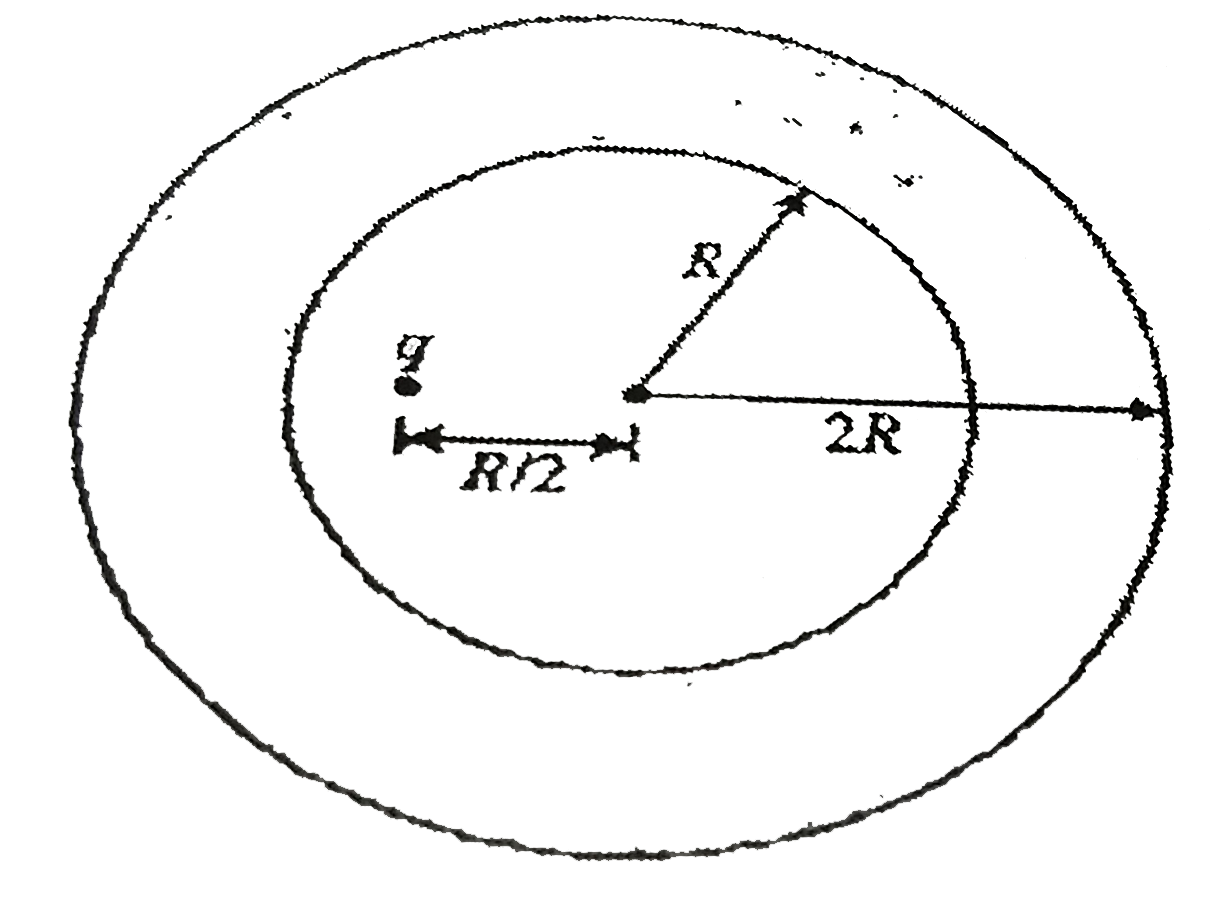
- Figure shows a cross-section ofa spherical metal shell of inner radius...
Text Solution
|
- A parallel plate capacitor of capacitance 3muF has total charge +15muC...
Text Solution
|
- An infinity long uniform line charge distribution of charge per unit l...
Text Solution
|
- A system consits of a ball of radus R carrying spherically symmetri...
Text Solution
|
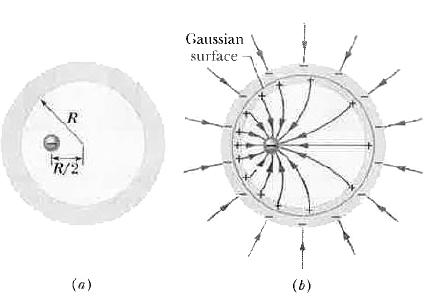 This distribution of negative charge is uniform because the shell is spherical and because the skewed distribution of positive charge on the inner wall cannot produce an electric field in the shell to affect the distribution of charge on the outer wall. Furthermore, these negative charges repel one another.
This distribution of negative charge is uniform because the shell is spherical and because the skewed distribution of positive charge on the inner wall cannot produce an electric field in the shell to affect the distribution of charge on the outer wall. Furthermore, these negative charges repel one another.