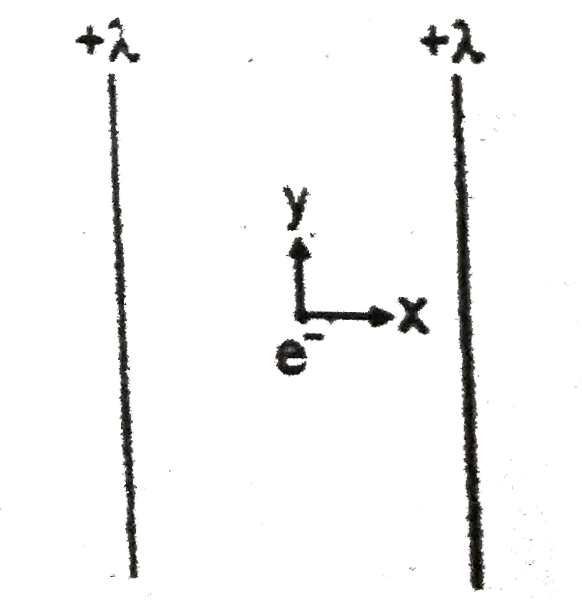A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
GAUSS' LAW
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise PRACTICE QUESTIONS (LINKED COMPREHENSION)|6 VideosGAUSS' LAW
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise PRACTICE QUESTIONS (INTEGER TYPE)|3 VideosGAUSS' LAW
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise PRACTICE QUESTIONS (SINGLE CORRECT CHOICE TYPE)|20 VideosFORCE AND MOTION-II
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise PRACTICE QUESTIONS (Integer Type)|1 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS : REFLECTION
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise PRACTICE QUESTIONS (Integer Type)|3 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems