Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
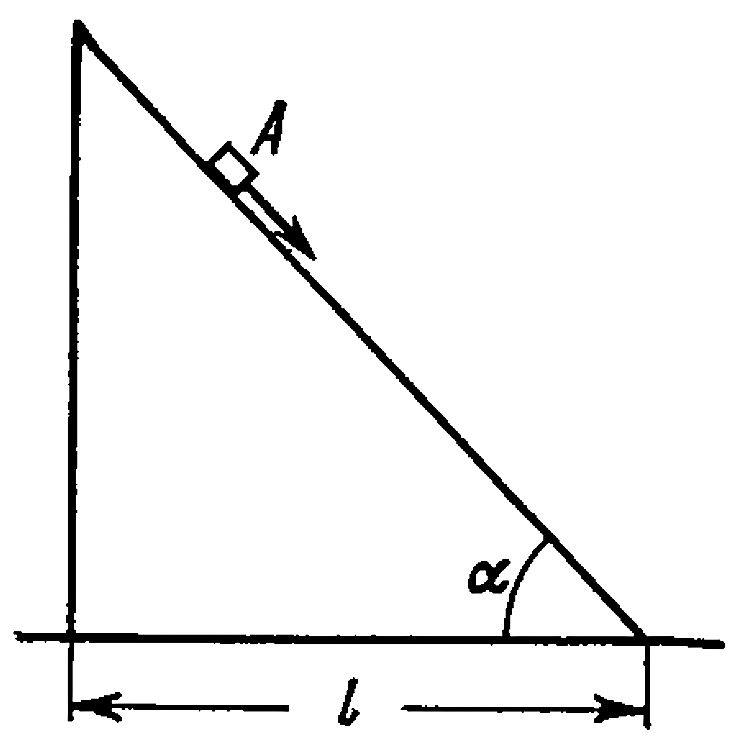
- A small body A starts sliding down from the top of a wedge (figure) wh...
Text Solution
|
- The minimum value of acceleration of wedge for which the block start s...
Text Solution
|
- A small body A starts sliding down from the top of a wedge (figure) wh...
Text Solution
|
- In the arrangement shown in figure the masses of the wedge M and the b...
Text Solution
|
- Starting from rest , a body slides down at 45^(@) inclined plane in tw...
Text Solution
|
- A block is at rest on an inclined plane making an angle alpha with the...
Text Solution
|
- When a block is placed on a wedge as shown in figure, the block starts...
Text Solution
|
- A small body A starts sliding down from the top of a wedge (see fig) w...
Text Solution
|
- As shown in the figure, a wedge of mass M is placed on a smooth inclin...
Text Solution
|