Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
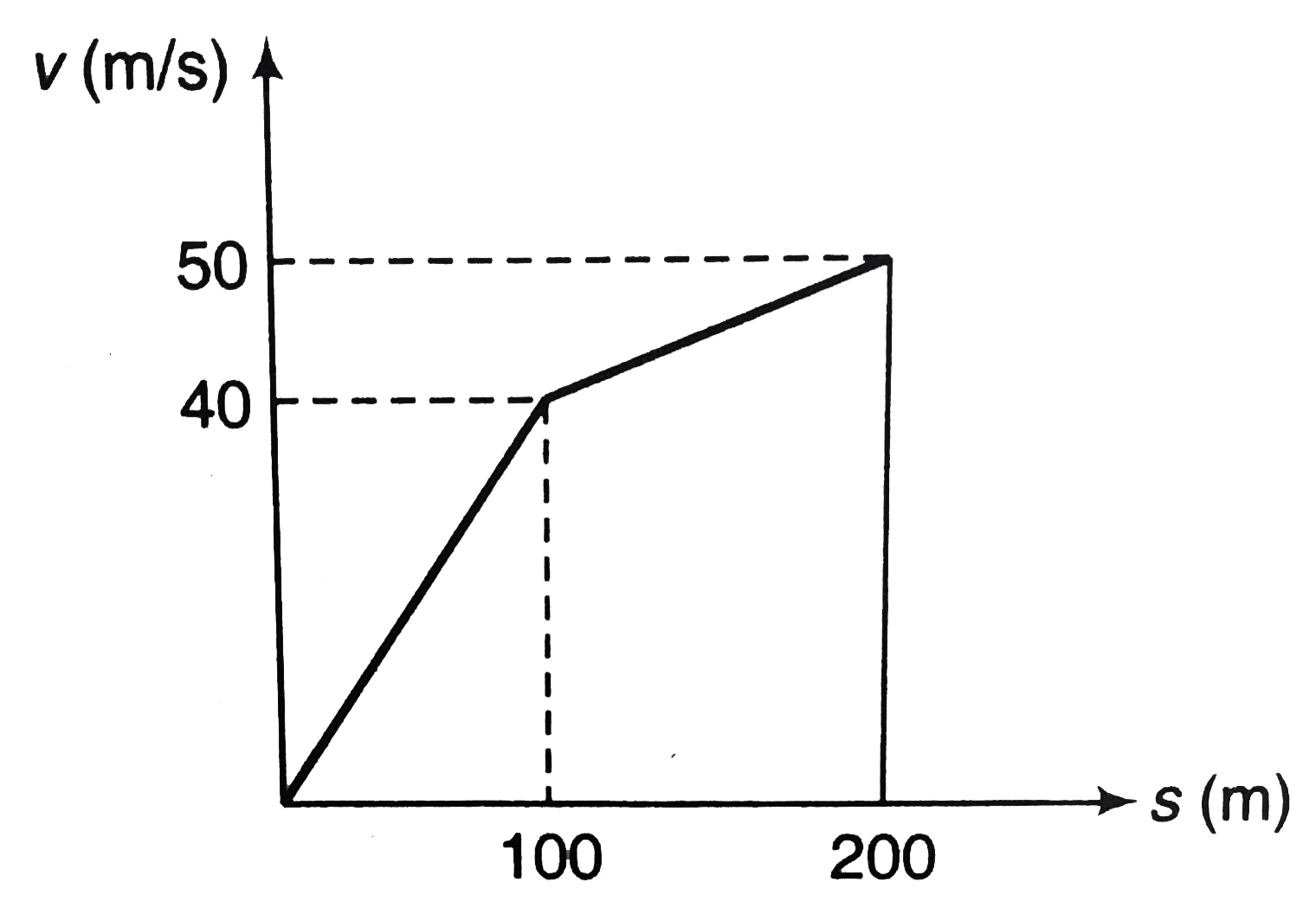
- The v-s graph for an airplane travelling on a straight runway is shown...
Text Solution
|
- A particle travels m a straight line, such that for a short time 2 s l...
Text Solution
|
- The v-s graph for an airplane travelling on a straight runway is shown...
Text Solution
|
- The v-s graph describing the motion of a motorcycle is shown in figure...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity-displacement for a fer plane on a straight runway is show...
Text Solution
|
- Acceleration (a) -displacement (s) graph of a particle moving in a str...
Text Solution
|
- Acceleration (a)-displacement(s) graph of a particle moving in a strai...
Text Solution
|
- The velocity –position graph of a particle moving along a straight lin...
Text Solution
|
- The minimum takeoff speed for a certain airplane in 75 m/s. What minim...
Text Solution
|