Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
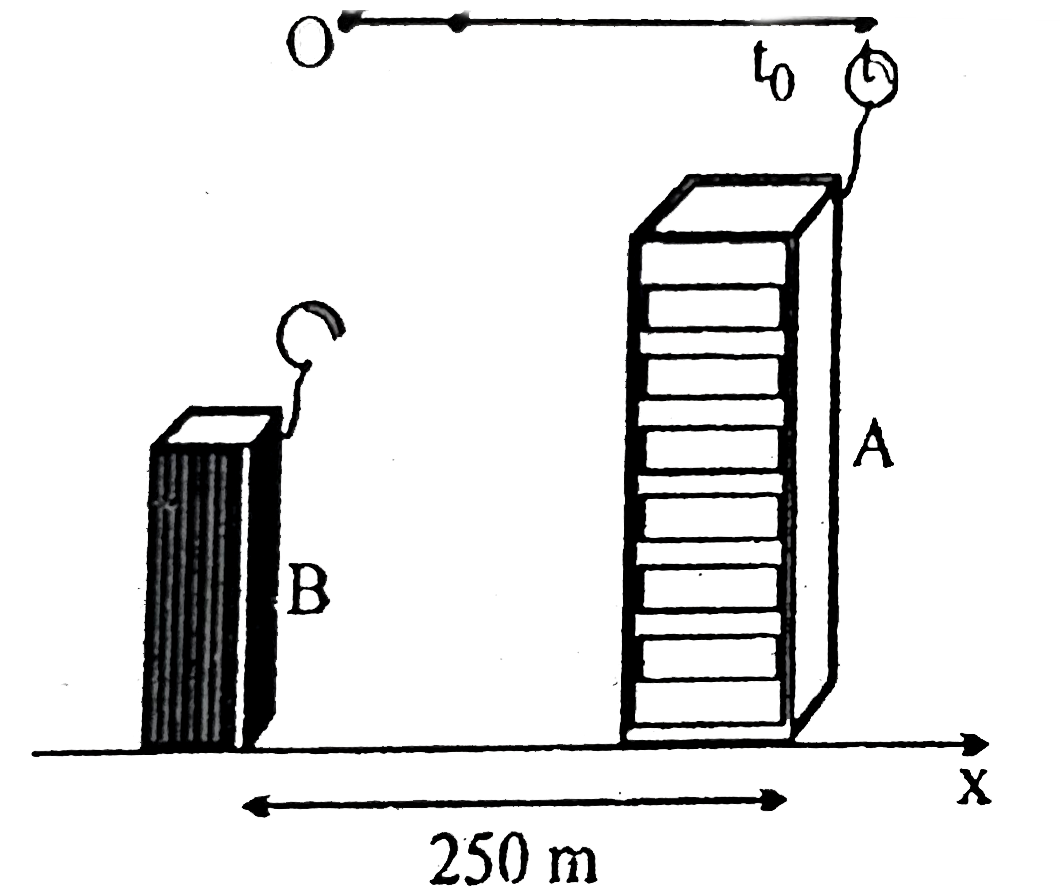
- Two ballons are simultaneously released from two buildings A and B. Ba...
Text Solution
|
- A balloon starts rising from the ground with an acceleration of 1.25ms...
Text Solution
|
- A balloon starts rising from the surface of the Earth. The ascertion r...
Text Solution
|
- Two ballons are simultaneously released from two buildings A and B. Ba...
Text Solution
|
- A balloon starts rising from the surface of the earth with vertical co...
Text Solution
|
- A balloon starts rising from the earth's surface. The ascension rate i...
Text Solution
|
- A balloon starts rising from the ground with a constant acceleration o...
Text Solution
|
- A balloon starts rising from the ground with a constant acceleration o...
Text Solution
|
- एक गुब्बारा 12 मी/से. के वेग से ऊपर उठ रहा है। गुब्बारे से एक पैकेट छो...
Text Solution
|