Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
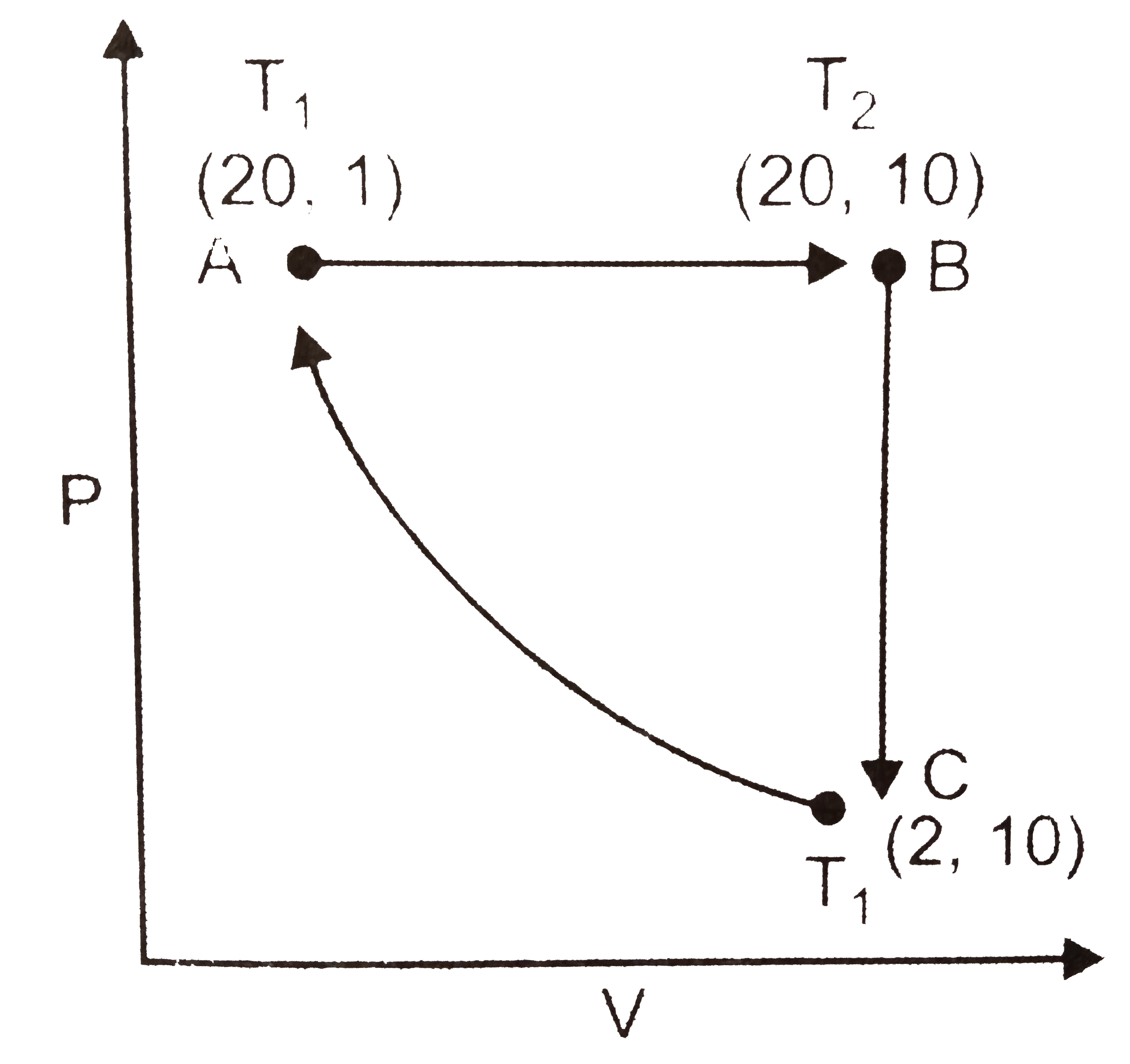
- One mole of a perfect gas is put through a cycle consisting of the fol...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a perfect gas is put through a cycle consisting of the fol...
Text Solution
|
- The work done in erge for the reversible expansion of 1 mole of an ide...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal gas at 27^(@) ,8.21 atm absorbs 420 cal of heat d...
Text Solution
|
- The workdone in ergs for the reversible expansion of one mole of an id...
Text Solution
|
- The amount of work done by 2 mole of an ideal gas at 298 K in reversib...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of an ideal gas expands from state-I (Atm , 20 litre) ...
Text Solution
|
- One mole of a prefect put throught a cycle consiting of the following ...
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the amount of work done by 2 mole of an ideal gas at 298 K i...
Text Solution
|