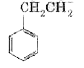
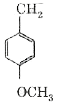
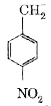
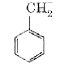A
B
C
D
Text Solution
AI Generated Solution
The correct Answer is:
Topper's Solved these Questions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise (Competition File) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS (with more than one correct answers)|10 VideosMOCK TEST-2
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise SECTION D|1 VideosREDOX REACTIONS
MODERN PUBLICATION|Exercise COMPETITION FILE (Objective Questions) (C. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS)|9 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
MODERN PUBLICATION-ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: BASIC PRINCIPLES AND TECHNIQUES-(Competition File) MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS ( based on the given. passage/comprehension )
- Passage Organic compounds mainly consist of covalent bonds. The elec...
Text Solution
|
- Passage Organic compounds mainly consist of covalent bonds. The elec...
Text Solution
|
- Passage Organic compounds mainly consist of covalent bonds. The elec...
Text Solution
|
- Passage Organic compounds mainly consist of covalent bonds. The elec...
Text Solution
|
- Passage Organic compounds mainly consist of covalent bonds. The elec...
Text Solution
|
- Passage Organic compounds mainly consist of covalent bonds. The elec...
Text Solution
|
- Passage Organic compounds mainly consist of covalent bonds. The elec...
Text Solution
|
- Passage Organic compounds mainly consist of covalent bonds. The elec...
Text Solution
|