Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS : REFRACTION
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise Check point|6 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS : REFRACTION
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise Problems|44 VideosGEOMETRICAL OPTICS : REFLECTION
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise PRACTICE QUESTIONS (Integer Type)|3 VideosGRAVITATION
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY|Exercise PRACTICE QUESTIONS (INTEGER TYPE)|4 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
RESNICK AND HALLIDAY-GEOMETRICAL OPTICS : REFRACTION-Practice questions(Integers)
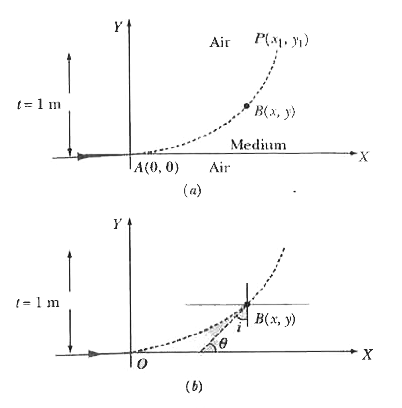
- A ray of light travelling in air is incident at grazing angle (incide...
Text Solution
|
- Let us consider simple microscope of a concave lens of power -10D and ...
Text Solution
|
- Radius of curvature of two surfaces of a glass convex lens is 20cm eac...
Text Solution
|
- A thin glass prism of angle 6^(@) of refractive index 1.5 is combined ...
Text Solution
|
- In a tank filled with a liquid of refractive index 5//3, a point sourc...
Text Solution
|