A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
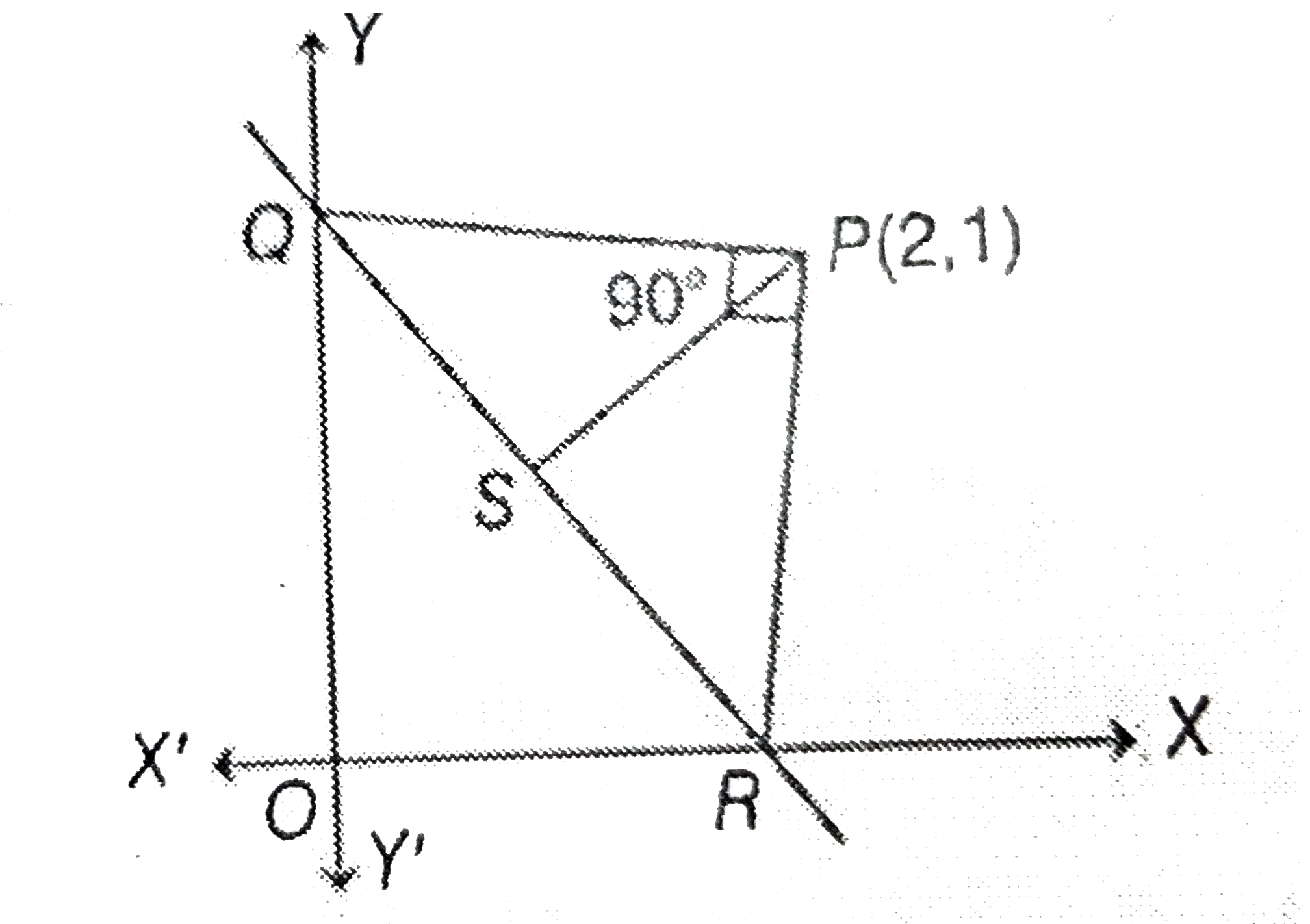
- 1. Let PQR be a right angled isosceles triangle, right angled at P (2,...
Text Solution
|
- PQR is a triangle right angled at P. If PQ=10cm and PR=24cm, find QR
Text Solution
|
- 1.Let PQR be a right angled isosceles triangle, right angled at P(2,1)...
Text Solution
|
- Let PQR be a right - angled isosceles triangle , right angled at P(2,1...
Text Solution
|
- माना PQR एक समकोण समद्विबाहु त्रिभुज है, जोकि बिन्दु P(2, 1) पर समक...
Text Solution
|
- मान लीजिए PQR एक समद्विबाहु समकोण P (2,1) पर समकोण है। यदि रेखा QR का ...
Text Solution
|
- Let PQR be a right-angled isosceles triangle right-angled at P(2, 1). ...
Text Solution
|
- Let PQR be a right angled isosceles triangle right angled at P(2,1) ...
Text Solution
|
- PQR is a triangle right angled at P. If PQ=10cm and PR=24cm, find QR
Text Solution
|