Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
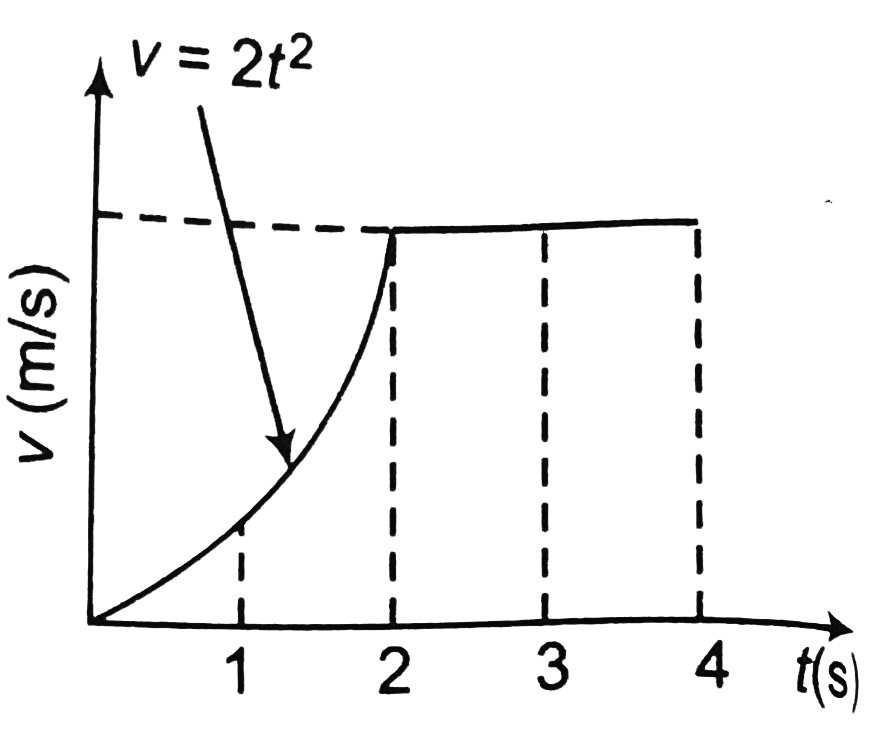
- A car begains from rest at time t = 0, and then acceleration along a s...
Text Solution
|
- A car begains from rest at time t = 0, and then acceleration along a s...
Text Solution
|
- A car starts from rest and moves with uniform acceleration a on a stra...
Text Solution
|
- A partical is moving in a straight line under constant acceleration 4 ...
Text Solution
|
- A car starts with constant acceleration a=2m//s^(2) at t=0. two coins ...
Text Solution
|
- At time t=0 s a car passes a point with velocity of 16 m//s and therea...
Text Solution
|
- A car is moving on a straight road. The velocity of the car varies wit...
Text Solution
|
- A car is moving on a straight road. The velocity of the car varies wit...
Text Solution
|
- An experimental car in fig (a) starts from rest and travels along a st...
Text Solution
|