Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT TELUGU-LAW OF MOTION-EXERCISE (ADDITIONAL EXERCISE)
- Figure shows the position-time graph of a body of mass 0.04 kg. Sugg...
Text Solution
|
- Figure shows a man standing stationary with respect to a horizontal c...
Text Solution
|
- A stone of mass m tied to the end of a string revolves in a vertical c...
Text Solution
|
- A helicopter of mass 1000 kg rises with a vertical acceleration of 15 ...
Text Solution
|
- A stream of water flowing horizontally with a speed of 15ms^(-1) push...
Text Solution
|
- Ten one-rupee coins are put on top of each other on a table. Each coi...
Text Solution
|
- An aircraft executes a horizontal loop at a speed of 720 km/h with i...
Text Solution
|
- A train runs along an unbanked circular track of radius 30 m at a spee...
Text Solution
|
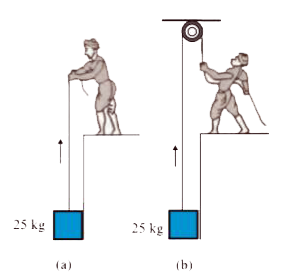
- A block of mass 25 kg is raised by a 50 kg man in two different ways a...
Text Solution
|
- A monkey of mass 40 kg climbs on a rope. which can stand a maximum ten...
Text Solution
|
- Two bodies A and B of masses 5 kg and 10 kg in contact with each othe...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass 15 kg is placed on a long trolley. The coefficient of ...
Text Solution
|
- The rear side of a truck is open and a box of 40 kg mass is placed 5 m...
Text Solution
|
- A disc revolves with a speed of 33/3 rev/min, and has a radius of 15...
Text Solution
|
- You may have seen in a circus a motorcyclist driving in vertical loops...
Text Solution
|
- A 70 kg man stands in contact against the inner wall of a hollow cylin...
Text Solution
|
- A thin circular loop of radius R rotates about its vertical diameter ...
Text Solution
|