Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Topper's Solved these Questions
SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
NCERT TELUGU|Exercise EXERCISES (TRUE OR FALSE)|5 VideosSYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION
NCERT TELUGU|Exercise EXERCISES (TRUE OR FALSE)|5 VideosOSCILLATIONS
NCERT TELUGU|Exercise Additional Exercises|6 VideosTHERMAL PROPERTIME OF MATTER
NCERT TELUGU|Exercise EXERCISES|30 Videos
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
NCERT TELUGU-SYSTEMS OF PARTICLES AND ROTATIONAL MOTION-EXERCISES
- (a) A child stands at the centre of a turntable with his two arms outs...
Text Solution
|
- A rope of negligible mass is wound round a hollow cylinder of mass 3 k...
Text Solution
|
- To maintain a rotor at a uniform angular speed or 200 rad s^(-1) an e...
Text Solution
|
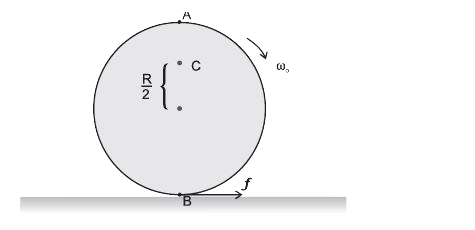
- From a uniform disk of radius R, a circular hole of radius R/2 is cut ...
Text Solution
|
- A metre stick is balanced on a knife edge at its centre. When two coin...
Text Solution
|
- A solid sphere rolls down two different inclined planes of the same he...
Text Solution
|
- A hoop of radius 2 m weighs 100 kg. It rolls along a horizontal floor ...
Text Solution
|
- The oxygen molecule has a mass of 5.30 × 10^(-26) kg and a moment of i...
Text Solution
|
- A solid cylinder rolls up an inclined plane of angle of inclination 30...
Text Solution
|
- As shown in Fig.7.40, the two sides of a step ladder BA and CA are 1.6...
Text Solution
|
- A man stands on a rotating platform, with his arms stretched horizonta...
Text Solution
|
- A bullet of mass 10 g and speed 500 m/s is fired into a door and gets ...
Text Solution
|
- Two discs of moments of inertia I(1) and I(2) about their respective a...
Text Solution
|
- (a) Prove the theorem of perpendicular axes. (b) Prove the theorem o...
Text Solution
|
- Prove the result that the velocity v of translation of a rolling body ...
Text Solution
|
- A disc rotating about its axis with angular speed ω(o) is placed light...
Text Solution
|
- Explain why friction is necessary to make the disc in Fig. 7.41 roll i...
Text Solution
|
- A solid disc and a ring, both of radius 10 cm are placed on a horizont...
Text Solution
|
- A cylinder of mass 10 kg and radius 15 cm is rolling perfectly on a pl...
Text Solution
|
- Separation of Motion of a system of particles into motion of the centr...
Text Solution
|