Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
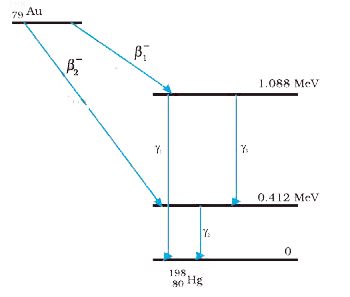
- Obtain the maximum kinetic energy of b-particles, and the radiation fr...
Text Solution
|
- Consider the beta decay ^198 Au rarr ^198 Hg ** + Beta^(-1) + vec v....
Text Solution
|
- Calculate the maximum energy that a beta particle can have in the foll...
Text Solution
|
- Obtain the maximum kinetic energy of beta-particles, and the radiation...
Text Solution
|
- नीचे दी गई क्षय योजना में gamma क्षयों की विकिरण आवृत्तियां एवं beta ...
Text Solution
|
- The nucleus .(10)^(23)Ne decays by beta - emission. Write down the bet...
Text Solution
|
- नीचे दी गयी क्षय योजना ( decay scheme ) में beta - कणो ...
Text Solution
|
- Obtain the maximum kinetic energy of beta- particle and the radiation ...
Text Solution
|
- Find the maximum energy that beta- particle may have in the following...
Text Solution
|