KEY IDEA
We use Eq. 2-2 for average velocity and Eq. 2-4 for instantaneous velocity, and work with distances in centimeters and times in seconds.
Calculations : (a) We plug into the given equation for `x` for `t=2.00s` and `t=3.00s` and obtain `x_(2)=21.75cm` and `x_(3) = 50.25cm`, respectively. The average velocity during the time interval `2.00 le t le 3.00s ` is
`v_("avg") = (Delta x)/(Delta t) = (50.25cm - 21.75cm)/(3.00s - 2.00s)`
which yields `v_("avg")=28.5 cm//s`.
(b) The instantaneous velocity is `v = (dx)/(dt) = 4.5 t^(2)`, which, at time `t=2.00s`, yields `v=(4.5)(2.00)^(2) =18.0cm//s`.
(c) At `t=3.00s`, the instantaneous velocity is
`v = (4.5)(3.00)^(2) =40.5cm//s`.
(d) At `t=2.50s`, the instantaneous velocity is
`v= (4.5)(2.50)^(2) = 28.1 cm//s`.
(e) Let `t_(m)` stand for the moment when the particle is midway between `x_(2)` and `x_(3)` ( that is, when the particle is at `x_(m)= (x_(2)+x_(3))//2=36cm`). Therefore,
`x_(m)= 9.75 + 1.5 t_(m)^(3) rArr t_(m) = 2.596`
in seconds. Thus, the instantaneous speed at this time is `v= 4.5(2.596)^(2) =30.3 cm//s`.
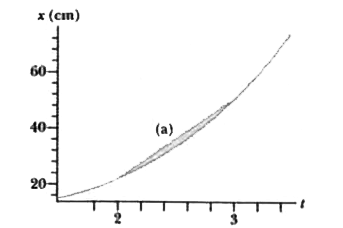
(f) The answer to part (a) is given by the slope of the straight line between `t=2` and `t=3` in this x-vs-t plot. The answers to parts (b), (c), (d), and (e) correspond to the slopes of tangent lines ( not shown but easily imagined ) to the curve at the appropriate points.