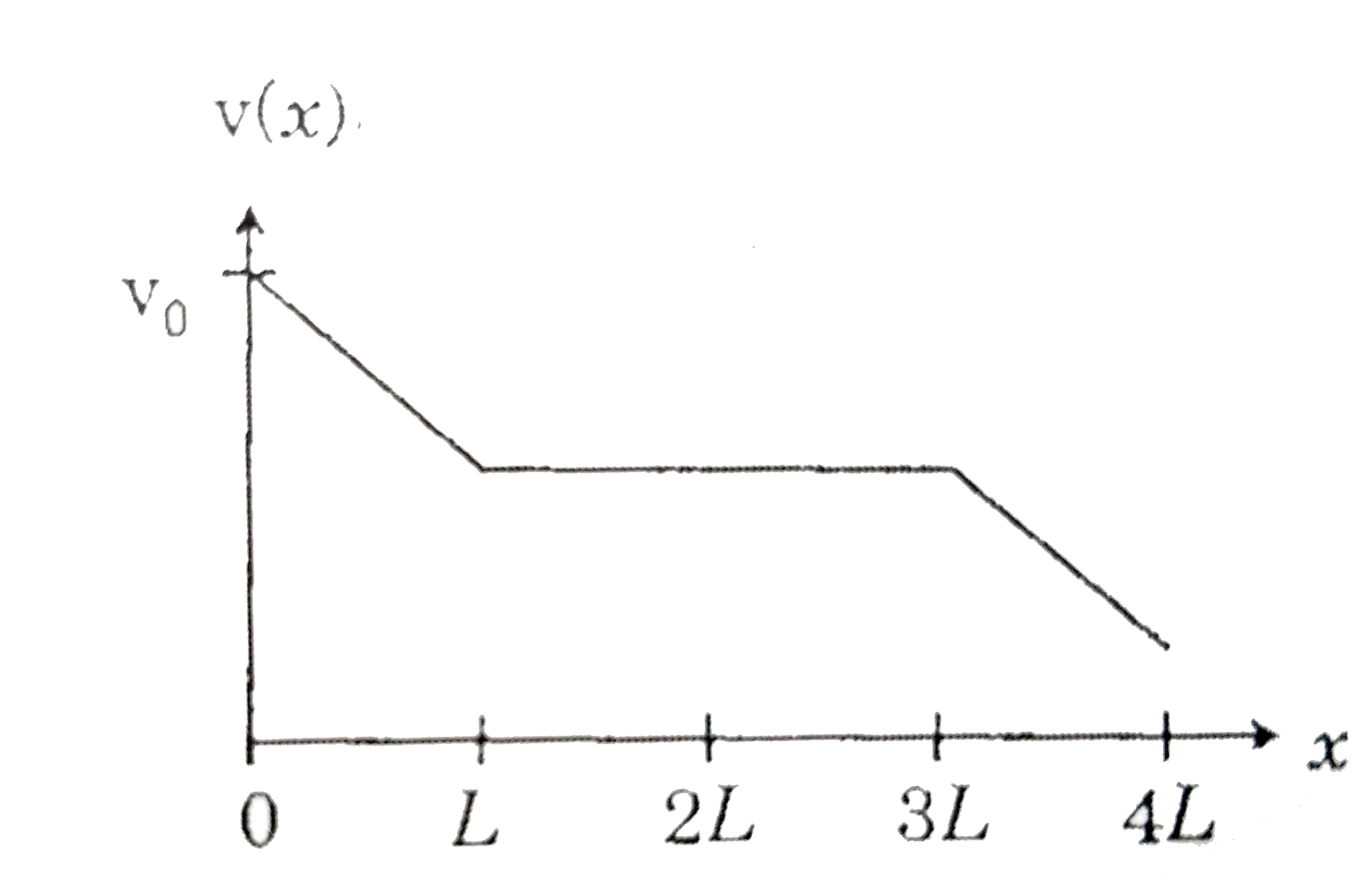
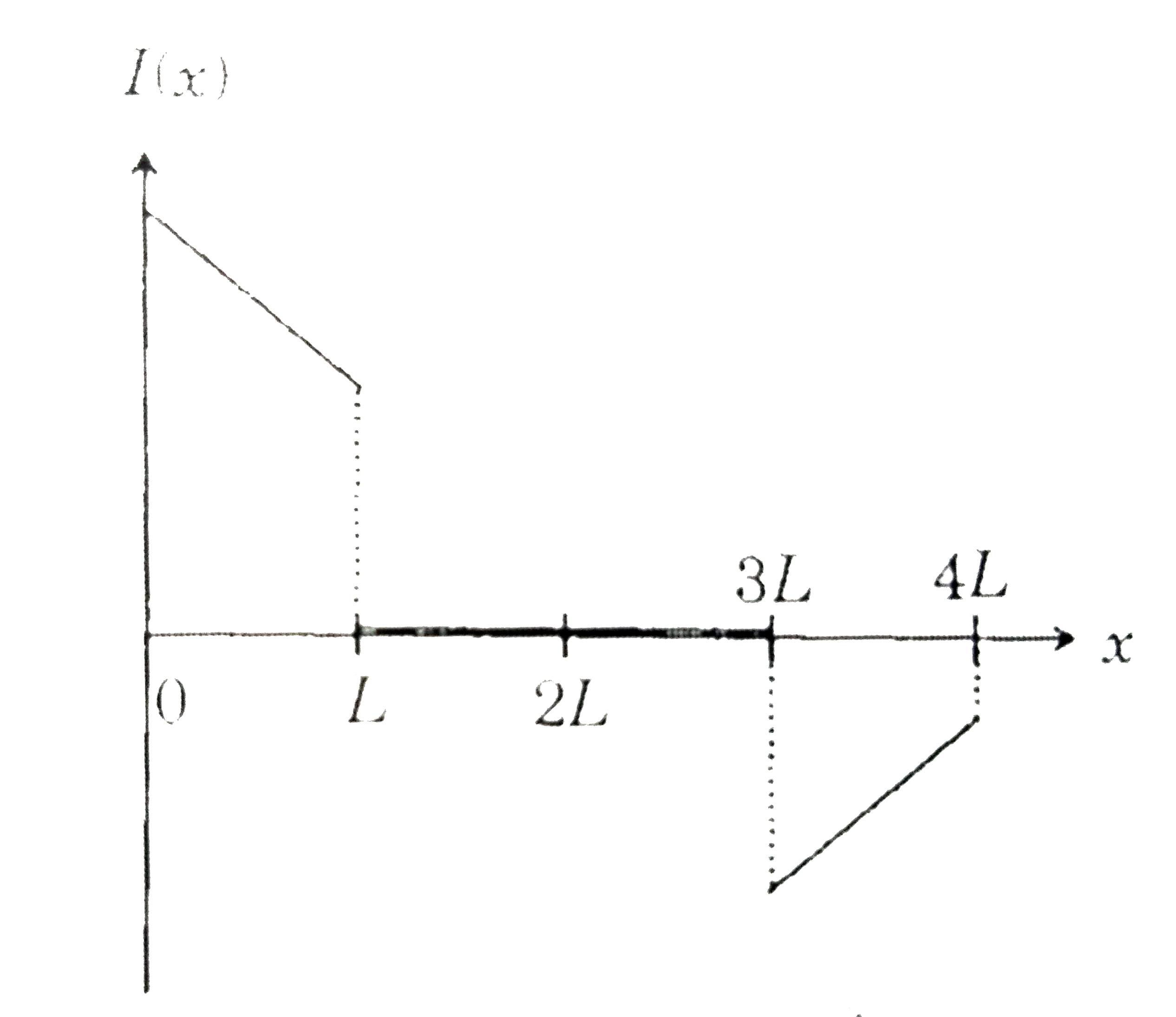
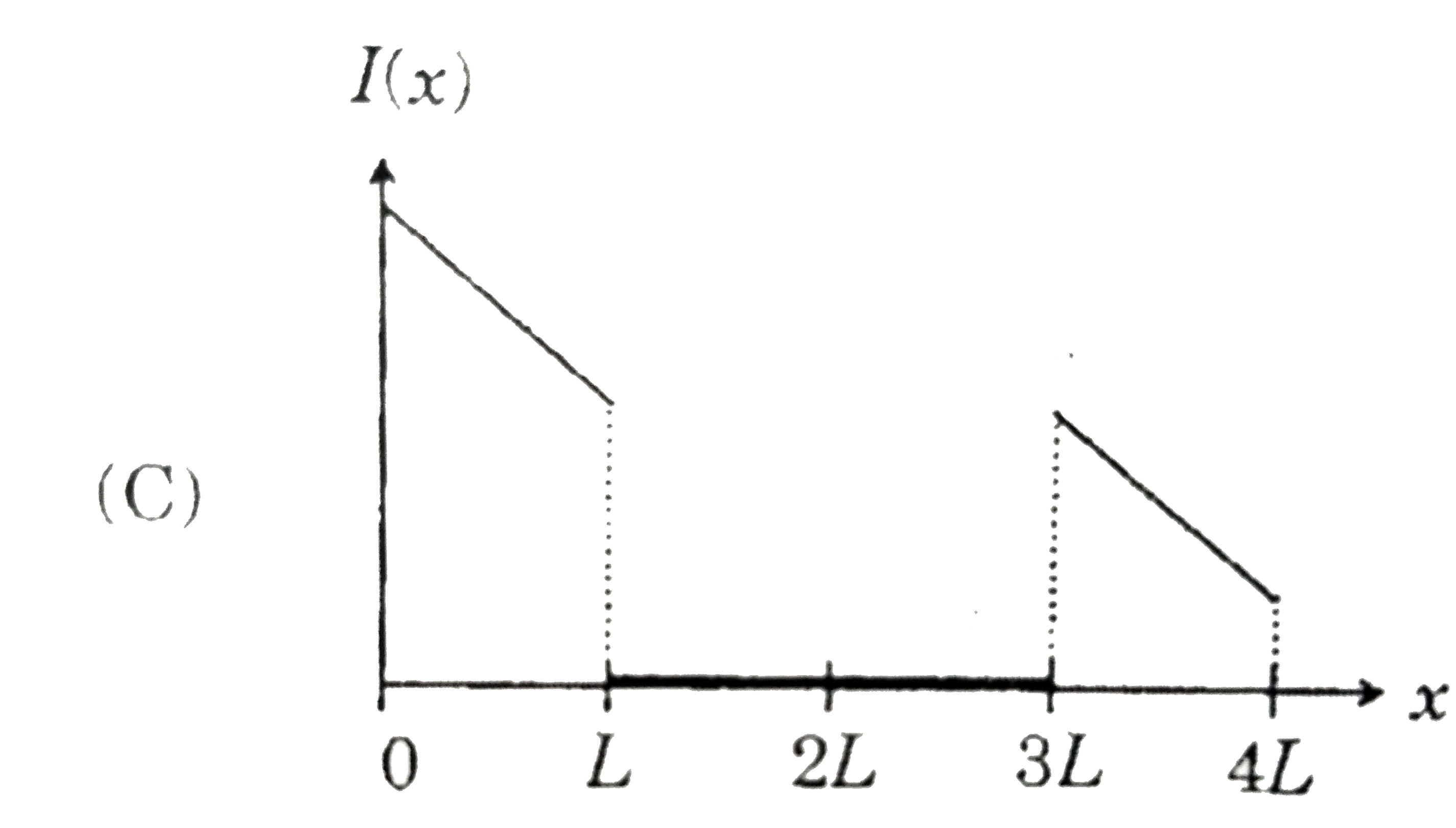
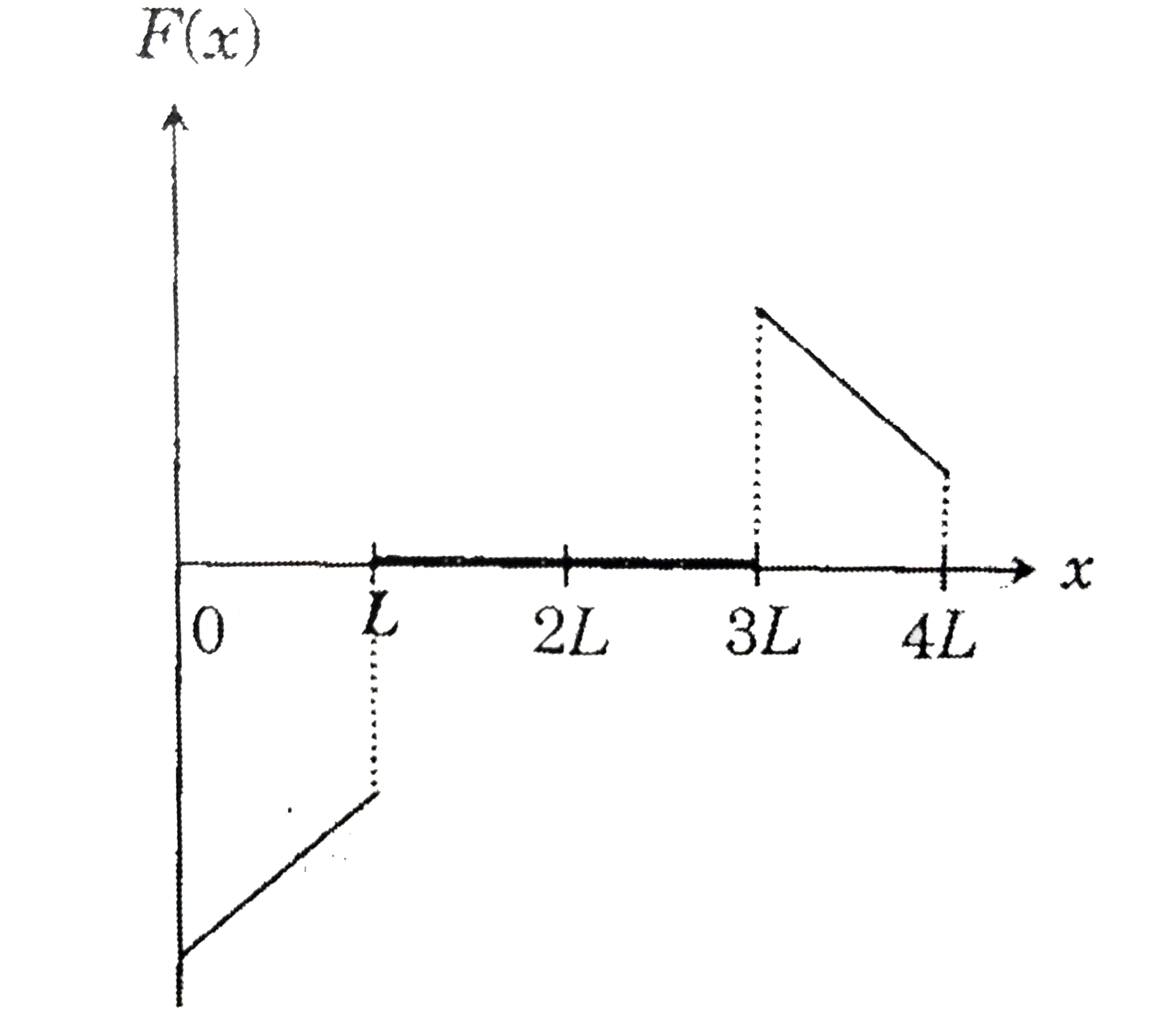
A
B
C
D
Text Solution
Verified by Experts
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- A rigid wire loop of square shape having side of length L and resistan...
Text Solution
|
- A rigid wire loop of square shape having side of length L and resistan...
Text Solution
|
- In the space shown a non-uniform magnetic field vec(B) = B(0)(1+x)(-ha...
Text Solution
|
- The magnetic field in a region is given by vec(B)=B(0)(1+(x)/(a))hat(k...
Text Solution
|
- A rigid wire loop of square shape having side of length L and resistan...
Text Solution
|
- The figure shows a loop of wire carrying a current i as shown. There e...
Text Solution
|
- एक चुंबकीय क्षेत्र vec(B) = ((B(0)y)/(a))hatk कागज के तल के लंबवत अं...
Text Solution
|
- A space is divided by the line AD into two regions. Region I is field ...
Text Solution
|
- A rectangular conducting loop of length l and breadth b enters a unifo...
Text Solution
|
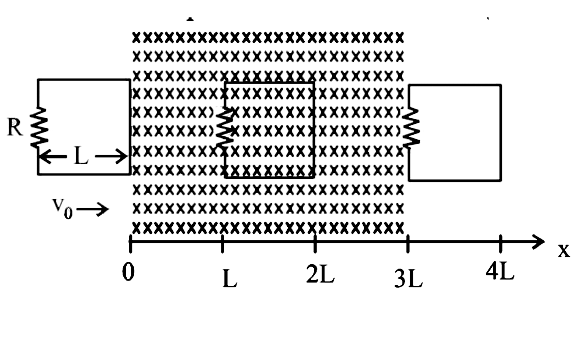 . Which of the following schematic plot(s) is (are) correct? (Ignore gravity)
. Which of the following schematic plot(s) is (are) correct? (Ignore gravity)