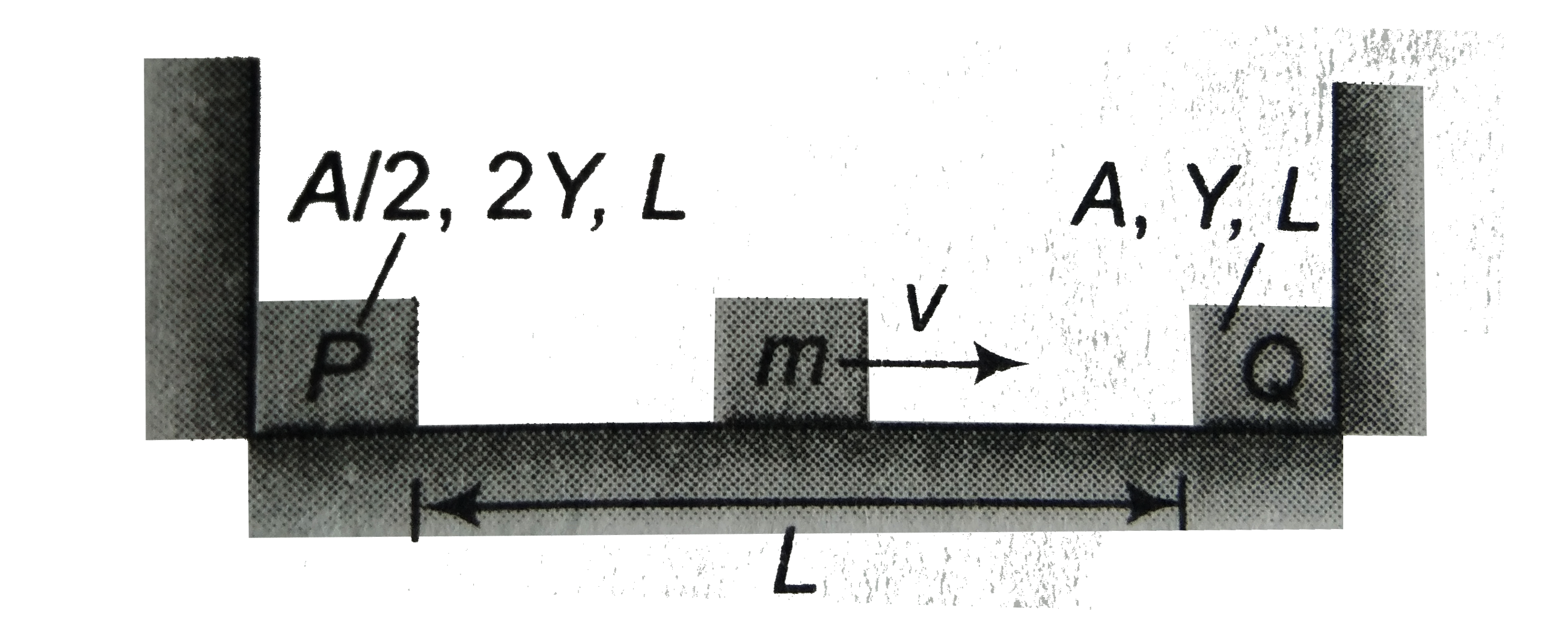Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
- In the given figure, two elastic rods P and Q are rigidly joined to en...
Text Solution
|
- In the given figure, two elastic rods P and Q are rigidly joined to en...
Text Solution
|
- A rod PQ of mass, area of cross section A, length l and young's modulu...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of mass M and length l is placed on a smooth- horizontal...
Text Solution
|
- A thin uniform rod of mass m and length l is kept on a smooth horizont...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of length L lies on a smooth horizontal table. The rod h...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of length L and mass M is pulled horizontally on a smoot...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of mass M and length L, area of cross section A is place...
Text Solution
|
- A uniform rod of mass M and length L, area of cross section A is place...
Text Solution
|