Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
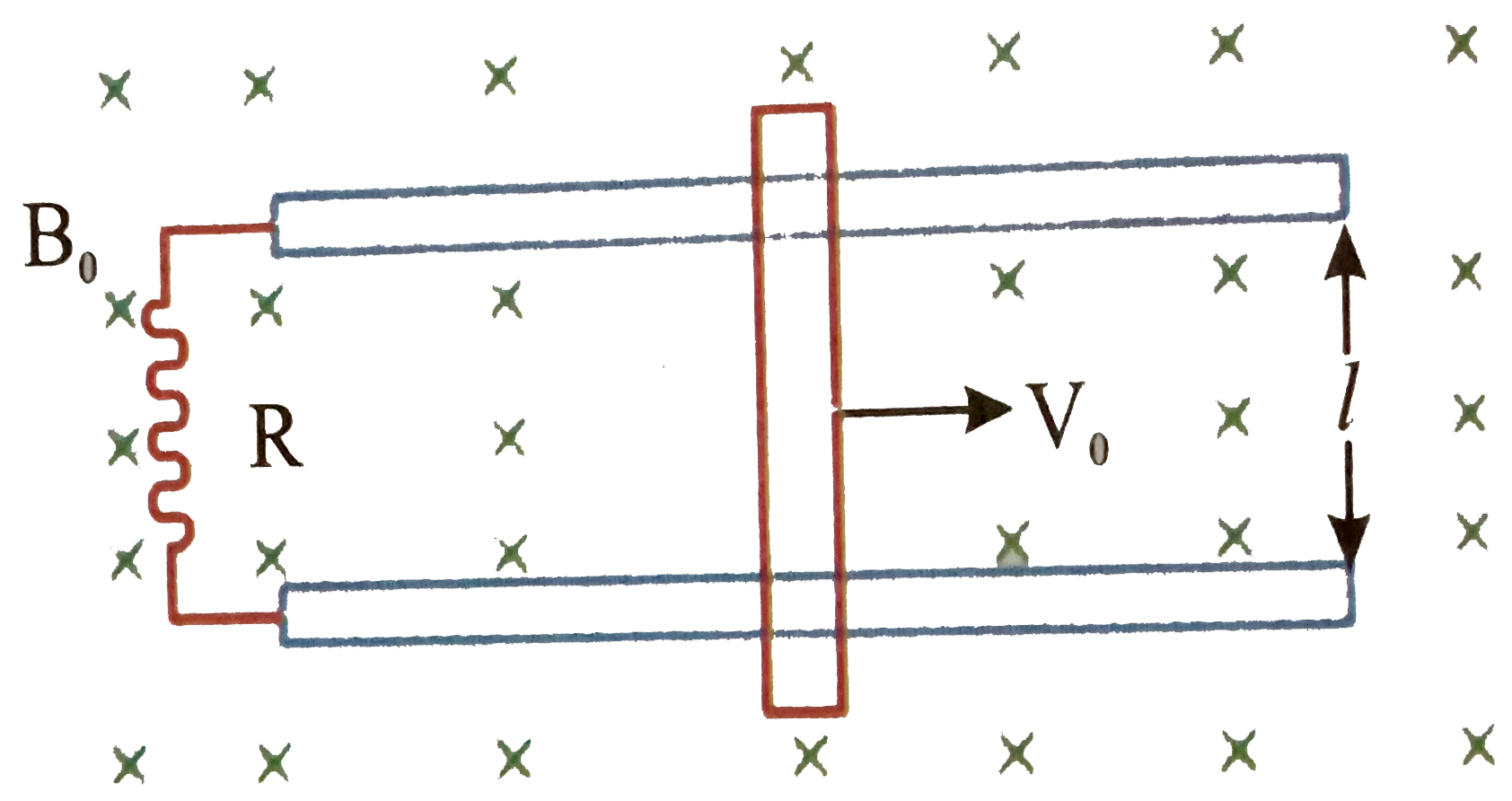
- A conducting bar mass m and length l moves on two frictionless paralle...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting rod shown in figure of mass m and length l moves on two f...
Text Solution
|
- Two straight conducting rails form a right angle where their ends are ...
Text Solution
|
- Electric field strength bar(E)=E(0)hat(i) and bar(B)=B(0)hat(i) exists...
Text Solution
|
- A bar of mass m and length l moves on two frictionless parallel rails ...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting bar mass m and length l moves on two frictionless paralle...
Text Solution
|
- Two long fixed parallel vertical conducting rails AB and CD are separa...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting movable rod AB lies across the frictionless parallel cond...
Text Solution
|
- A conducting bar of mass m and length l moves on two frictionless para...
Text Solution
|