Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
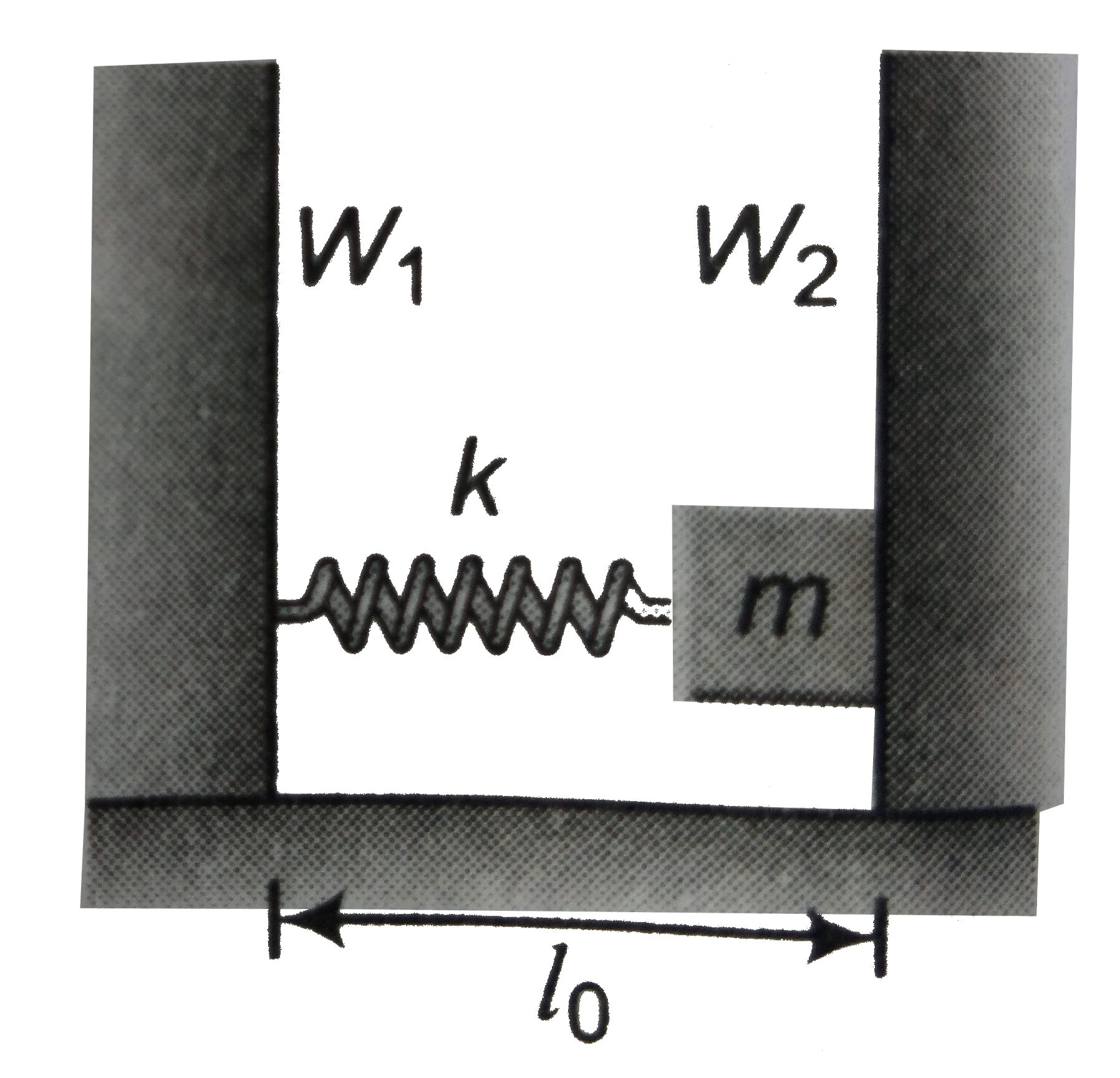
- In the figure shown, a spring mass system is placed on a horizontal sm...
Text Solution
|
- A block of mass m is attached to one end of a mass less spring of spri...
Text Solution
|
- In the figure shown, a spring mass system is placed on a horizontal sm...
Text Solution
|
- A string with one end fixed on a rigid wall, passing over a fixed fric...
Text Solution
|
- A Bead of mass m is attached to one end of a spring of natural length ...
Text Solution
|
- One end of a light spring of natural length 4m and spring constant 170...
Text Solution
|
- A spring of force constant K rests on a smooth floor, with one end fix...
Text Solution
|
- One end of a spring of force constant K is fixed to a vertical wall an...
Text Solution
|
- A spring of mass m lies on a smooth table. One, end of it is clamped t...
Text Solution
|