A bicycle has pedal rods of length `16 cm` connected to sprocketed disc of radius `10 cm`. The bicycle wheels are `70 cm` in diameter and the chain runs over a gear of radius `4cm`. The speed of the cycle is constant and the cyclist applies `100 N` for, that is always perpendicular to the pedal rod, as shown in figure. Assume tension in the lower part of chain is negligible. The cyclist is peddling at a constant rate of two revolutions per second. Assume that the force applied by other foot is zero when one foot is exerting `100 N` force. Neglect friction within cycle parts and the rolling friction.
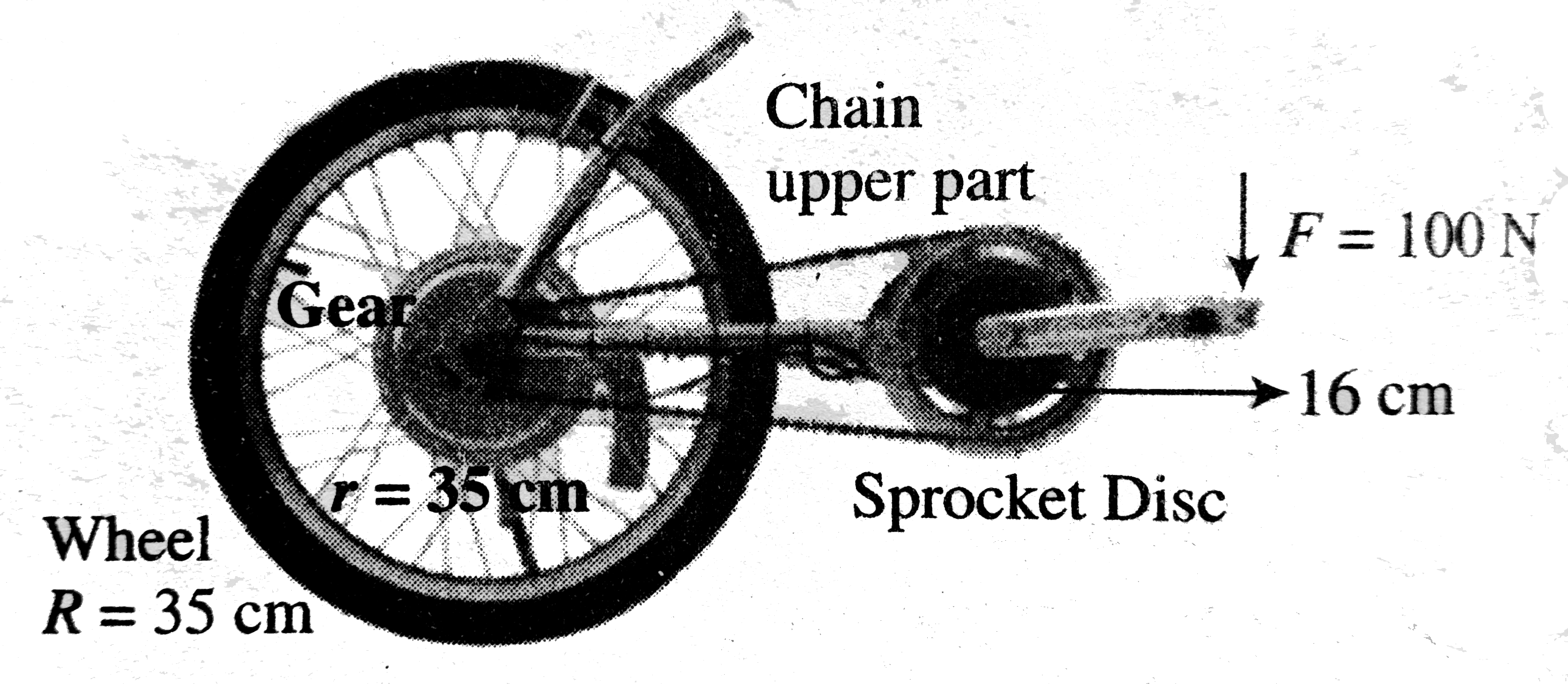
Net torque on the rear wheel of the bicycle is equal to
A bicycle has pedal rods of length `16 cm` connected to sprocketed disc of radius `10 cm`. The bicycle wheels are `70 cm` in diameter and the chain runs over a gear of radius `4cm`. The speed of the cycle is constant and the cyclist applies `100 N` for, that is always perpendicular to the pedal rod, as shown in figure. Assume tension in the lower part of chain is negligible. The cyclist is peddling at a constant rate of two revolutions per second. Assume that the force applied by other foot is zero when one foot is exerting `100 N` force. Neglect friction within cycle parts and the rolling friction.
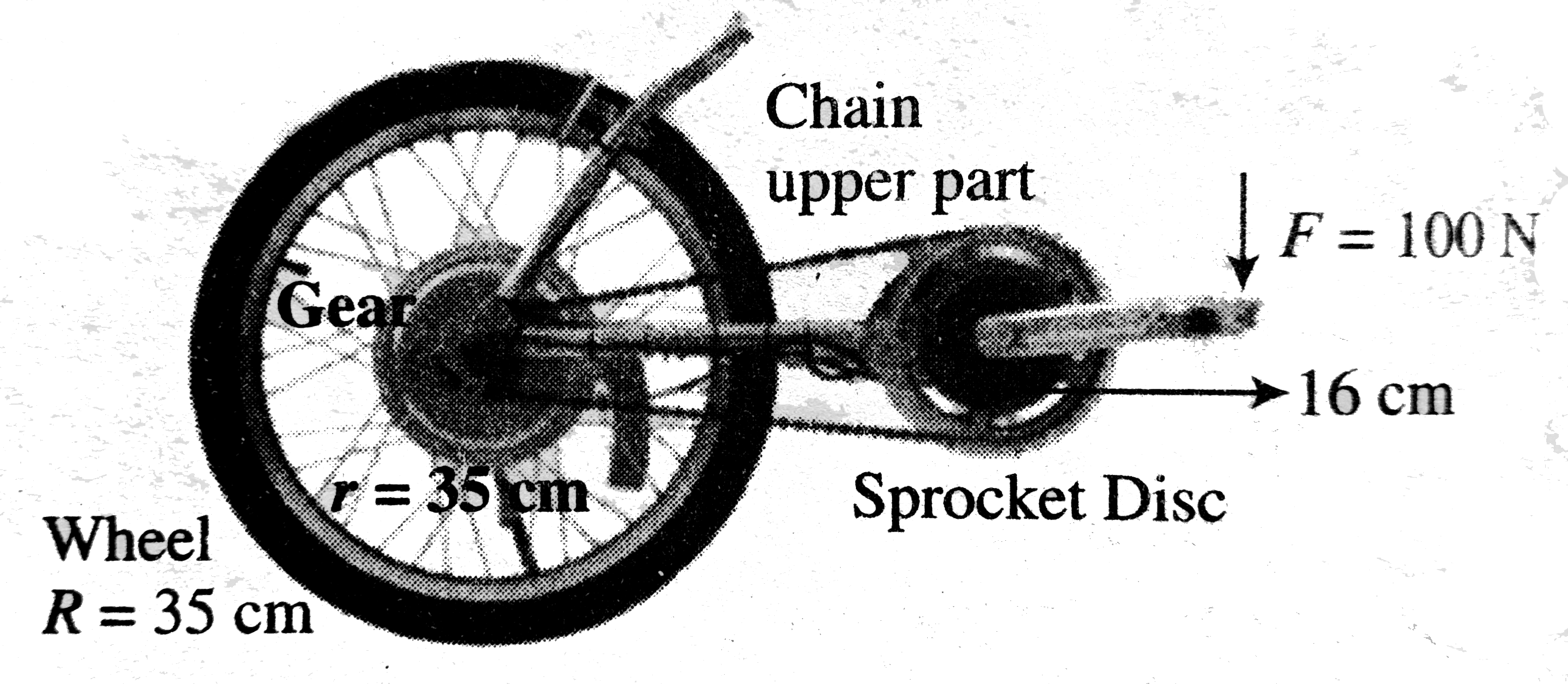
Net torque on the rear wheel of the bicycle is equal to
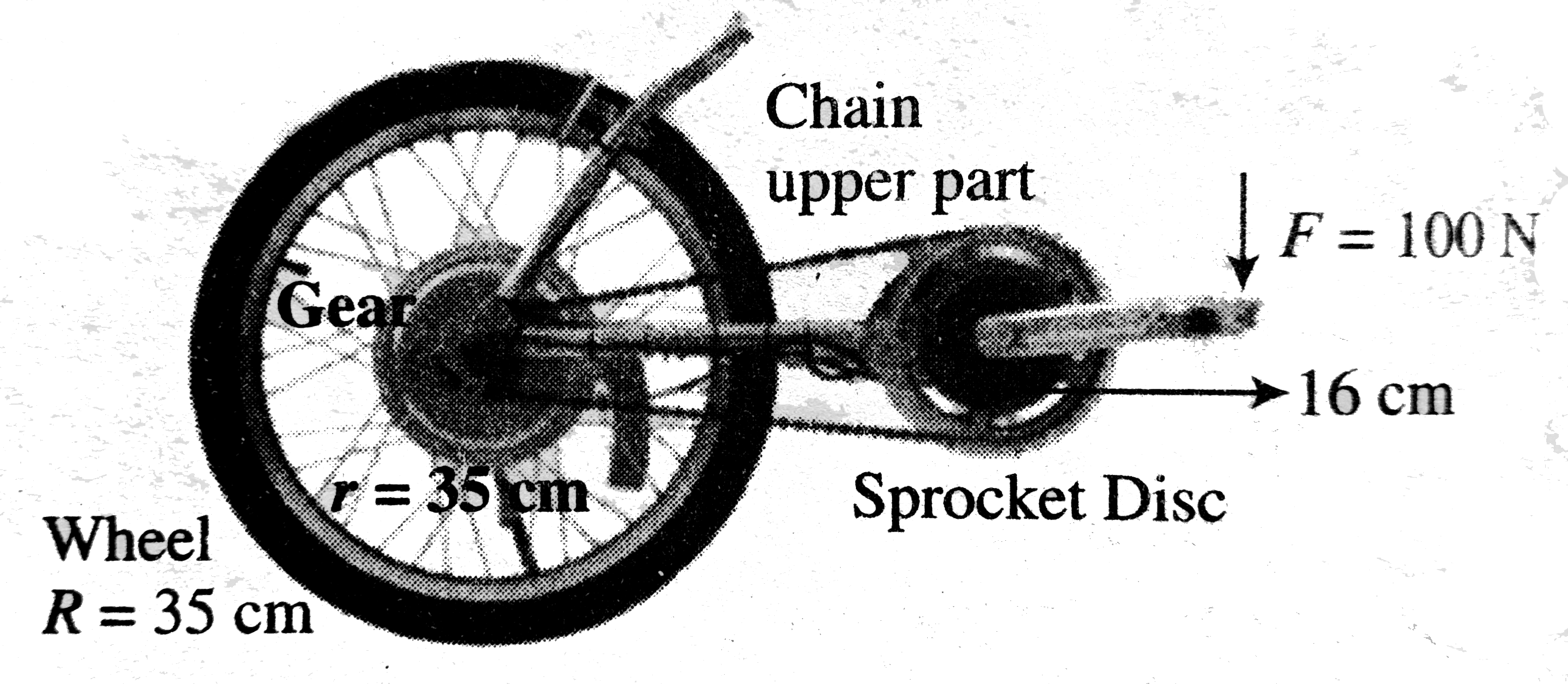
Net torque on the rear wheel of the bicycle is equal to
Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
A bicycle has pedal rods of length 16 cm connected to sprocketed disc of radius 10 cm . The bicycle wheels are 70 cm in diameter and the chain runs over a gear of radius 4cm . The speed of the cycle is constant and the cyclist applies 100 N for, that is always perpendicular to the pedal rod, as shown in figure. Assume tension in the lower part of chain is negligible. The cyclist is peddling at a constant rate of two revolutions per second. Assume that the force applied by other foot is zero when one foot is exerting 100 N force. Neglect friction within cycle parts and the rolling friction. The speed of the bicycle is
A bicycle has pedal rods of length 16 cm connected to sprocketed disc of radius 10 cm . The bicycle wheels are 70 cm in diameter and the chain runs over a gear of radius 4cm . The speed of the cycle is constant and the cyclist applies 100 N for, that is always perpendicular to the pedal rod, as shown in figure. Assume tension in the lower part of chain is negligible. The cyclist is peddling at a constant rate of two revolutions per second. Assume that the force applied by other foot is zero when one foot is exerting 100 N force. Neglect friction within cycle parts and the rolling friction. The speed of the bicycle is
A bicycle has pedal rods of length 16 cm connected to sprocketed disc of radius 10 cm . The bicycle wheels are 70 cm in diameter and the chain runs over a gear of radius 4cm . The speed of the cycle is constant and the cyclist applies 100 N for, that is always perpendicular to the pedal rod, as shown in figure. Assume tension in the lower part of chain is negligible. The cyclist is peddling at a constant rate of two revolutions per second. Assume that the force applied by other foot is zero when one foot is exerting 100 N force. Neglect friction within cycle parts and the rolling friction. The tension in the upper portion of the chain is equal to
A bicycle has pedal rods of length 16 cm connected to sprocketed disc of radius 10 cm . The bicycle wheels are 70 cm in diameter and the chain runs over a gear of radius 4cm . The speed of the cycle is constant and the cyclist applies 100 N for, that is always perpendicular to the pedal rod, as shown in figure. Assume tension in the lower part of chain is negligible. The cyclist is peddling at a constant rate of two revolutions per second. Assume that the force applied by other foot is zero when one foot is exerting 100 N force. Neglect friction within cycle parts and the rolling friction. The tension in the upper portion of the chain is equal to
A bicycle has pedal rods of length 16 cm connected to sprocketed disc of radius 10 cm . The bicycle wheels are 70 cm in diameter and the chain runs over a gear of radius 4cm . The speed of the cycle is constant and the cyclist applies 100 N for, that is always perpendicular to the pedal rod, as shown in figure. Assume tension in the lower part of chain is negligible. The cyclist is peddling at a constant rate of two revolutions per second. Assume that the force applied by other foot is zero when one foot is exerting 100 N force. Neglect friction within cycle parts and the rolling friction. The net force of the friction on the rear wheel due to the road is:
A bicycle has pedal rods of length 16 cm connected to sprocketed disc of radius 10 cm . The bicycle wheels are 70 cm in diameter and the chain runs over a gear of radius 4cm . The speed of the cycle is constant and the cyclist applies 100 N for, that is always perpendicular to the pedal rod, as shown in figure. Assume tension in the lower part of chain is negligible. The cyclist is peddling at a constant rate of two revolutions per second. Assume that the force applied by other foot is zero when one foot is exerting 100 N force. Neglect friction within cycle parts and the rolling friction. The net force of the friction on the rear wheel due to the road is:
A bicycle has pedal rods of length 16 cm connected to sprocketed disc of radius 10 cm . The bicycle wheels are 70 cm in diameter and the chain runs over a gear of radius 4cm . The speed of the cycle is constant and the cyclist applies 100 N for, that is always perpendicular to the pedal rod, as shown in figure. Assume tension in the lower part of chain is negligible. The cyclist is peddling at a constant rate of two revolutions per second. Assume that the force applied by other foot is zero when one foot is exerting 100 N force. Neglect friction within cycle parts and the rolling friction. The power delivered by the cyclist is equal to
A bicycle has pedal rods of length 16 cm connected to sprocketed disc of radius 10 cm . The bicycle wheels are 70 cm in diameter and the chain runs over a gear of radius 4cm . The speed of the cycle is constant and the cyclist applies 100 N for, that is always perpendicular to the pedal rod, as shown in figure. Assume tension in the lower part of chain is negligible. The cyclist is peddling at a constant rate of two revolutions per second. Assume that the force applied by other foot is zero when one foot is exerting 100 N force. Neglect friction within cycle parts and the rolling friction. The power delivered by the cyclist is equal to
Recommended Questions
- A bicycle has pedal rods of length 16 cm connected to sprocketed disc ...
Text Solution
|
- A bicycle has pedal rods of length 16 cm connected to sprocketed disc ...
Text Solution
|
- A bicycle has pedal rods of length 16 cm connected to sprocketed disc ...
Text Solution
|
- A bicycle has pedal rods of length 16 cm connected to sprocketed disc ...
Text Solution
|
- A bicycle has pedal rods of length 16 cm connected to sprocketed disc ...
Text Solution
|
- A bicycle has pedal rods of length 16 cm connected to sprocketed disc ...
Text Solution
|
- The number of teeth in the crank wheel and free wheel of a bicycle, c...
Text Solution
|
- किसी बाइसकिल के पहिये की त्रिज्या 70 सेमि है| बताईये की पहिये के एक लग...
Text Solution
|
- A cyclist rides up a hill at a constant velocity. Determine the power ...
Text Solution
|