Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
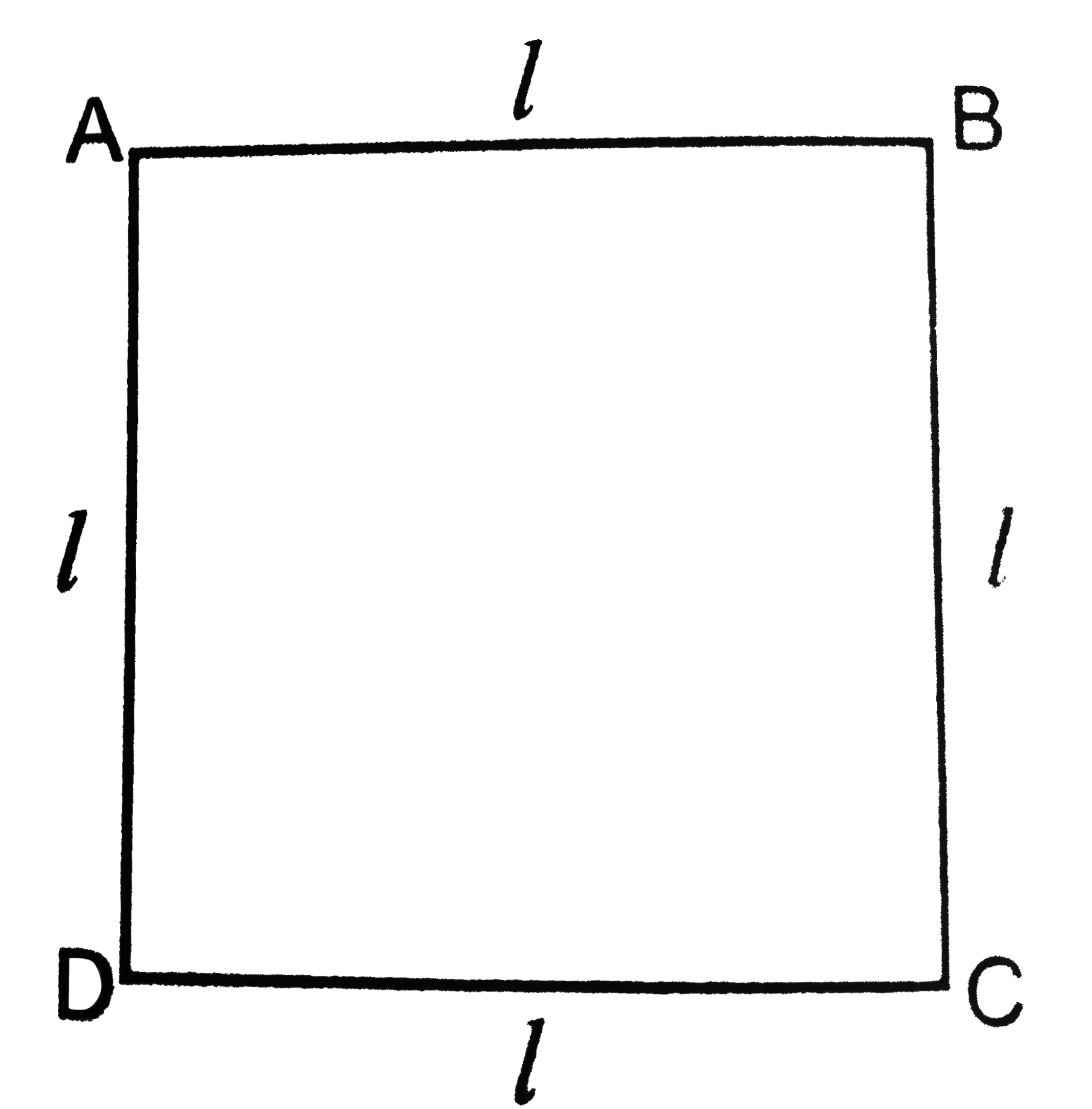
- A praticle moves along the side of a squre fo length (l) starting from...
Text Solution
|
- A particle starts from a pointn A and travels along the solid curve sh...
Text Solution
|
- A praticle moves along the side of a squre fo length (l) starting from...
Text Solution
|
- Three particles A,B and C and situated at the vertices of an equilater...
Text Solution
|
- Velocity time graphs of particles A and B moving along x-axis are show...
Text Solution
|
- A particle is moving with uniform acceleration along a straight line A...
Text Solution
|
- A particle, moving with uniform acceleration along a straight line ABC...
Text Solution
|
- किसी निश्चित दिशा में अनुदिश चल रहे किसी कण का चाल-समय ग्राफ चित्र मे...
Text Solution
|
- x -अक्ष पर चलते हुए एक कण का स्थान x = At ^ 3 + B t ^ 2 +...
Text Solution
|
 .
.