Similar Questions
Explore conceptually related problems
Recommended Questions
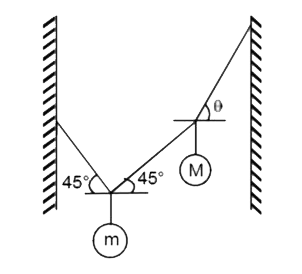
- Two masses m and M are attached to the strings as shown in the figure....
Text Solution
|
- A blocked of mass m is attached with two strings as shown in figure .D...
Text Solution
|
- Two masses m and M are attached with strings as shown. For the system ...
Text Solution
|
- In the system shown in the figure all surfaces are smooth, pulley and ...
Text Solution
|
- A block A of mass M on an inclined surface and a small weight B of mas...
Text Solution
|
- Two masses m and M are attached to the strings as shown in the figure....
Text Solution
|
- As shown in figure pulley is ideal and strings are massless.If mass m ...
Text Solution
|
- Two masses m and M are attached to the strings as shown in the figure....
Text Solution
|
- Two block each of mass 'm' are attached with two elastic strings as sh...
Text Solution
|